Predictive Value of Soluble PD-1, PD-L1, VEGFA, CD40 Ligand and CD44 for Nivolumab Therapy in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Case-Control Study
- PMID: 32085544
- PMCID: PMC7072584
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12020473
Predictive Value of Soluble PD-1, PD-L1, VEGFA, CD40 Ligand and CD44 for Nivolumab Therapy in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Case-Control Study
Abstract
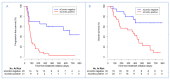
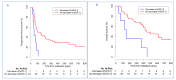
A large interindividual variability has been observed in anti Programmed cell Death 1 (anti-PD1) therapies efficacy. The aim of this study is to assess the correlation of soluble PD-1 (sPD-1), soluble Programmed cell Death Ligand 1 (sPD-L1), Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A (VEGFA), soluble CD40 ligand (sCD40L) and soluble CD44 (sCD44), with survival in nivolumab-treated metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Plasma biomarkers were assayed at baseline and after two cycles of nivolumab. A cut-off of positivity for sPD-1, sPD-L1 and sCD40L expressions was defined as a plasma level above the lower limit of quantification. Baseline sPD-1 and sPD-L1 levels were subsequently analyzed in a control group of EGFR-mutated (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) NSCLC patients. Association between survival and biomarkers was investigated using Cox proportional hazard regression model. Eighty-seven patients were included (51 nivolumab-treated patients, 36 in EGFR-mutated group). In nivolumab group, baseline sPD-1, sPD-L1 and sCD40L were positive for 15(29.4%), 27(52.9%) and 18(50%) patients, respectively. We defined a composite criteria (sCombo) corresponding to sPD-1 and/or sPD-L1 positivity for each patient. In nivolumab group, baseline sCombo positivity was associated with shorter median progression-free survival (PFS) (78 days 95%CI (55-109) vs. 658 days (222-not reached); HR: 4.12 (1.95-8.71), p = 0.0002) and OS (HR: 3.99(1.63-9.80), p = 0.003). In multivariate analysis, baseline sCombo independently correlated with PFS (HR: 2.66 (1.17-6.08), p = 0.02) but not OS. In EGFR-mutated group, all patients were baseline sCombo positive; therefore this factor was not associated with survival. After two cycles of nivolumab, an increased or stable sPD-1 level independently correlated with longer PFS (HR: 0.49, 95%CI (0.30-0.80), p = 0.004) and OS (HR: 0.39, 95%CI (0.21-0.71), p = 0.002). VEGFA, sCD40L and sCD44 did not correlate with survival. We propose a composite biomarker using sPD-1and sPDL-1 to predict nivolumab efficacy in NSCLC patients. A larger validation study is warranted.
Keywords: Immune checkpoint inhibitors; NSCLC; PD-1; biomarkers; nivolumab.
Conflict of interest statement
B.B. has served on advisory boards and received honoraria AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Leo Pharma and Pfizer. D.D. has received fees for consulting and educational activities from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp and Dohme, AstraZeneca Medimmune, Roche/Genentech. F.G. has received travel accommodation and research grant from Bristol-Myers Squibb. J.Ale. has received grants and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Roche/Genentech, Novartis, Ipsen, and Jansen. P.B.-R. has served on advisory board for and received honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb. M.W. has received fees for consulting, advisory board and educational activities from Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche, MSD, Amgen, BMS, Astra Zeneca; and her institution received clinical trials support from AstraZeneca. All other authors (M.T.M., A.J., E.G.-L., E.F., M.A., K.L., C.T., N.K., J.Arr., A.T.-S., H.B., A.M.-L., M.V.) have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Planchard D., Popat S., Kerr K., Novello S., Smit E.F., Faivre-Finn C., Mok T.S., Reck M., Van Schil P.E., Hellmann M.D., et al. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up †. Ann Oncol. 2018;29:192–237. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy275. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

