5-(Carbamoylmethylene)-oxazolidin-2-ones as a Promising Class of Heterocycles Inducing Apoptosis Triggered by Increased ROS Levels and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Breast and Cervical Cancer
- PMID: 32085547
- PMCID: PMC7168333
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines8020035
5-(Carbamoylmethylene)-oxazolidin-2-ones as a Promising Class of Heterocycles Inducing Apoptosis Triggered by Increased ROS Levels and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Breast and Cervical Cancer
Abstract
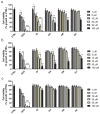
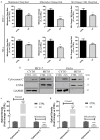
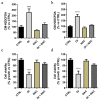
Oxazolidinones are antibiotics that inhibit protein synthesis by binding the 50S ribosomal subunit. Recently, numerous worldwide researches focused on their properties and possible involvement in cancer therapy have been conducted. Here, we evaluated in vitro the antiproliferative activity of some 5-(carbamoylmethylene)-oxazolidin-2-ones on MCF-7 and HeLa cells. The tested compounds displayed a wide range of cytotoxicity on these cancer cell lines, measured by MTT assay, exhibiting no cytotoxicity on non-tumorigenic MCF-10A cells. Among the nine tested derivatives, four displayed a good anticancer potential. Remarkably, OI compound showed IC50 values of 17.66 and 31.10 µM for MCF-7 and HeLa cancer cells, respectively. Furthermore, we assessed OI effect on the cell cycle by FACS analysis, highlighting a G1 phase arrest after 72 h, supported by a low expression level of Cyclin D1 protein. Moreover, mitochondrial membrane potential was reduced after OI treatment driven by high levels of ROS. These findings demonstrate that OI treatment can inhibit MCF-7 and HeLa cell proliferation and induce apoptosis by caspase-9 activation and cytochrome c release in the cytosol. Hence, 5-(carbamoylmethylene)-oxazolidin-2-ones have a promising anticancer activity, in particular, OI derivative could represent a good candidate for in vivo further studies and potential clinical use.
Keywords: ROS; anticancer compounds; apoptosis; mitochondria; oxazolidinones.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Cancer Fact Sheet N 297. [(accessed on 25 November 2019)]; Available online: www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

