Flexible Players within the Sheaths: The Intrinsically Disordered Proteins of Myelin in Health and Disease
- PMID: 32085570
- PMCID: PMC7072810
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9020470
Flexible Players within the Sheaths: The Intrinsically Disordered Proteins of Myelin in Health and Disease
Erratum in
-
Correction: Raasakka, A.; Kursula, P. Flexible Players within the Sheaths: The Intrinsically Disordered Proteins of Myelin in Health and Disease. Cells 2020, 9, 470.Cells. 2022 Feb 14;11(4):662. doi: 10.3390/cells11040662. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35203407 Free PMC article.
Abstract
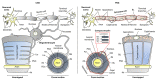
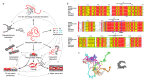
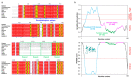
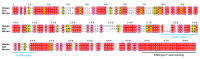
Myelin ensheathes selected axonal segments within the nervous system, resulting primarily in nerve impulse acceleration, as well as mechanical and trophic support for neurons. In the central and peripheral nervous systems, various proteins that contribute to the formation and stability of myelin are present, which also harbor pathophysiological roles in myelin disease. Many myelin proteins have common attributes, including small size, hydrophobic segments, multifunctionality, longevity, and regions of intrinsic disorder. With recent advances in protein biophysical characterization and bioinformatics, it has become evident that intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) are abundant in myelin, and their flexible nature enables multifunctionality. Here, we review known myelin IDPs, their conservation, molecular characteristics and functions, and their disease relevance, along with open questions and speculations. We place emphasis on classifying the molecular details of IDPs in myelin, and we correlate these with their various functions, including susceptibility to post-translational modifications, function in protein-protein and protein-membrane interactions, as well as their role as extended entropic chains. We discuss how myelin pathology can relate to IDPs and which molecular factors are potentially involved.
Keywords: intrinsically disordered protein; multiple sclerosis; myelin; myelination; peripheral neuropathies; protein folding; protein–membrane interaction; protein–protein interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Lundgaard I., Luzhynskaya A., Stockley J.H., Wang Z., Evans K.A., Swire M., Volbracht K., Gautier H.O.B., Franklin R.J.M., ffrench-Constant C., et al. Neuregulin and BDNF Induce a Switch to NMDA Receptor-Dependent Myelination by Oligodendrocytes. PLoS. Biol. 2013;11:e1001743. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001743. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Young J.Z. The functioning of the giant nerve fibres of the squid. J. Exp. Biol. 1938;15:170–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

