Staphylococcus aureus Epidemiology in Wildlife: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 32085586
- PMCID: PMC7168057
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics9020089
Staphylococcus aureus Epidemiology in Wildlife: A Systematic Review
Abstract
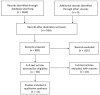
Staphylococcus aureus is a common bacterial colonizer of humans and a variety of animal species. Many strains have zoonotic potential, moving between humans and animals, including livestock, pets, and wildlife. We examined publications reporting on S. aureus presence in a variety of wildlife species in order to more cohesively review distribution of strains and antibiotic resistance in wildlife. Fifty-one studies were included in the final qualitative synthesis. The most common types documented included ST398, ST425, ST1, ST133, ST130, and ST15. A mix of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible strains were noted. A number of molecular types were identified that were likely to be found in wildlife species, including those that are commonly found in humans or other animal species (including livestock). Additional research should include follow-up in geographic areas that are under-sampled in this study, which is dominated by European studies.
Keywords: antibiotic resistance; environment; molecular typing; zoonosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources