Sick leave, disability, and mortality in acute hepatic porphyria: a nationwide cohort study
- PMID: 32085780
- PMCID: PMC7035738
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-019-1273-4
Sick leave, disability, and mortality in acute hepatic porphyria: a nationwide cohort study
Abstract
Background: Acute hepatic porphyria (AHP) consists of three rare metabolic disorders. We investigated the risk of long-term sick leave, disability pension, and premature death in individuals with AHP compared to the general population.
Methods: In a nationwide cohort study from 1992 to 2017, records of 333 persons (total person-years = 6728) with a confirmed AHP diagnosis were linked to several national compulsory registries (reference population = 5,819,937). We conducted survival analyses to assess additional risk.
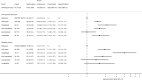
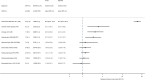
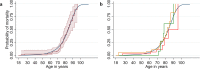
Results: Persons with AHP had higher risks of accessing long-term sick leave (adjusted hazard ratio (aHR): 1.5, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.3, 1.7) and disability pension (aHR: 1.9, CI: 1.5, 2.4). The risk was highest in persons who had been hospitalised for acute attacks, while no additional risk was observed in asymptomatic AHP gene mutation carriers. The median age when accessing disability pension was 45 years, 21 years younger than the general population. AHP was associated with increased risk of mortality due to hepatocellular carcinoma (adjusted mortality rate ratio (aMRR): 84.4, CI: 37.8, 188.2), but no overall increased risk of premature death was observed.
Conclusions: Persons with symptomatic AHP were at increased risk of accessing long-term sick leave and disability pension but not of premature death.
Keywords: Acute hepatic porphyria; Acute intermittent porphyria; Disability pension; Hereditary coproporphyria; Long-term sick leave; Morbidity; Mortality; Premature death; Variegate porphyria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Jeans JB, Savik K, Gross CR, Weimer MK, Bossenmaier IC, Pierach CA, et al. Mortality in patients with acute intermittent porphyria requiring hospitalization: a United States case series. Am J Med Genet. 1996;65(4):269–273. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19961111)65:4<269::AID-AJMG4>3.0.CO;2-K. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Strand LJ, Felsher BF, Redeker AG, Marver HS. Heme biosynthesis in intermittent acute prophyria: decreased hepatic conversion of porphobilinogen to porphyrins and increased delta aminolevulinic acid synthetase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970;67(3):1315–1320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1315. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mykletun M, Aarsand AK, Stole E, Villanger JH, Tollanes MC, Baravelli C, et al. Porphyrias in Norway. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2014;134(8):831–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

