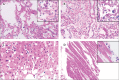
Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome
- PMID: 32085846
- PMCID: PMC7164771
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X
Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome
Erratum in
-
Correction to Lancet Respir Med 2020; 8: 420-22.Lancet Respir Med. 2020 Apr;8(4):e26. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30085-0. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Lancet Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 32109426 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Figures

Comment in
-
Recovery from SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with serum BDNF restoration.J Infect. 2020 Sep;81(3):e79-e81. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.06.038. Epub 2020 Jun 20. J Infect. 2020. PMID: 32569603 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Histopathologic Findings in the Explant Lungs of a Patient With COVID-19 Treated With Bilateral Orthotopic Lung Transplant.Transplantation. 2020 Nov;104(11):e329-e331. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003412. Transplantation. 2020. PMID: 33122591 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

