Characterization of heteromeric complexes between chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 and α1-adrenergic receptors utilizing intermolecular bioluminescence resonance energy transfer assays
- PMID: 32085899
- PMCID: PMC7937191
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.094
Characterization of heteromeric complexes between chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 and α1-adrenergic receptors utilizing intermolecular bioluminescence resonance energy transfer assays
Abstract
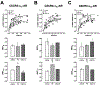
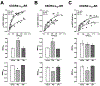
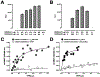
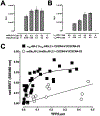
Recently, we reported that chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 (CXCR4) heteromerizes with α1-adrenergic receptors (AR) on the cell surface of vascular smooth muscle cells, through which the receptors cross-talk. Direct biophysical evidence for CXCR4:α1-AR heteromers, however, is lacking. Here we utilized bimolecular luminescence/fluorescence complementation (BiLC/BiFC) combined with intermolecular bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) assays in HEK293T cells to evaluate CXCR4:α1a/b/d-AR heteromerization. Atypical chemokine receptor 3 (ACKR3) and metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (mGlu1R) were utilized as controls. BRET between CXCR4-RLuc (Renilla reniformis) and enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (EYFP)-tagged ACKR3 or α1a/b/d-ARs fulfilled criteria for constitutive heteromerization. BRET between CXCR4-RLuc and EYFP or mGlu1R-EYFP were nonspecific. BRET50 for CXCR4:ACKR3 and CXCR4:α1a/b/d-AR heteromers were comparable. Stimulation of cells with phenylephrine increased BRETmax of CXCR4:α1a/b/d-AR heteromers without affecting BRET50; stimulation with CXCL12 reduced BRETmax of CXCR4:α1a-AR heteromers, but did not affect BRET50 or BRETmax/50 for CXCR4:α1b/d-AR. A peptide analogue of transmembrane domain (TM) 2 of CXCR4 reduced BRETmax of CXCR4:α1a/b/d-AR heteromers and increased BRET50 of CXCR4:α1a/b-AR interactions. A TM4 analogue of CXCR4 did not alter BRET. We observed CXCR4, α1a-AR and mGlu1R homodimerization by BiFC/BiLC, and heteromerization of homodimeric CXCR4 with proto- and homodimeric α1a-AR by BiFC/BiLC BRET. BiFC/BiLC BRET for interactions between homodimeric CXCR4 and homodimeric mGlu1R was nonspecific. Our findings suggest that the heteromerization affinity of CXCR4 for ACKR3 and α1-ARs is comparable, provide evidence for conformational changes of the receptor complexes upon agonist binding and support the concept that proto- and oligomeric CXCR4 and α1-ARs constitutively form higher-order hetero-oligomeric receptor clusters.
Keywords: Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay; Bimolecular luminescence complementation assay; G protein-coupled receptor heteromers; Hetero-oligomer; Homodimer; Stromal cell-derived factor 1α.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
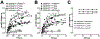
References
-
- Alexander SP, Christopoulos A, Davenport AP, Kelly E, Marrion NV, Peters JA, Faccenda E, Harding SD, Pawson AJ, Sharman JL, Southan C, Davies JA, Collaborators C, THE CONCISE GUIDE TO PHARMACOLOGY 2017/18: G protein-coupled receptors, Br J Pharmacol 174 Suppl 1 (2017) S17–S129. 10.1111/bph.13878. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

