Polyproline-rich peptides associated with Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase tetramers
- PMID: 32087110
- PMCID: PMC7065271
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109007
Polyproline-rich peptides associated with Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase tetramers
Abstract
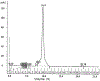
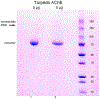
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) terminates cholinergic neurotransmission by hydrolyzing acetylcholine. The collagen-tailed AChE tetramer is a product of 2 genes, ACHE and ColQ. The AChE tetramer consists of 4 identical AChE subunits and one polyproline-rich peptide, whose function is to hold the 4 AChE subunits together. Our goal was to determine the amino acid sequence of the polyproline-rich peptide(s) in Torpedo californica AChE (TcAChE) tetramers to aid in the analysis of images that will be acquired by cryo-EM. Collagen-tailed AChE was solubilized from Torpedo californica electric organ, converted to 300 kDa tetramers by digestion with trypsin, and purified by affinity chromatography. Polyproline-rich peptides were released by denaturing the TcAChE tetramers in a boiling water bath, and reducing disulfide bonds with dithiothreitol. Carbamidomethylated peptides were separated from TcAChE protein on a spin filter before they were analyzed by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry on a high resolution Orbitrap Fusion Lumos mass spectrometer. Of the 64 identified collagen-tail (ColQ) peptides, 60 were from the polyproline-rich region near the N-terminus of ColQ. The most abundant proline-rich peptides were SVNKCCLLTPPPPPMFPPPFFTETNILQE, at 40% of total mass-spectral signal intensity, and SVNKCCLLTPPPPPMFPPPFFTETNILQEVDLNNLPLEIKPTEPSCK, at 27% of total intensity. The high abundance of these 2 peptides makes them candidates for the principal form of the polyproline-rich peptide in the trypsin-treated TcAChE tetramers.
Keywords: Mass spectrometry; Polyproline; Tetramer; Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Polyproline tetramer organizing peptides in fetal bovine serum acetylcholinesterase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Apr;1834(4):745-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.01.009. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23352838 Free PMC article.
-
The mammalian gene of acetylcholinesterase-associated collagen.J Biol Chem. 1997 Sep 5;272(36):22840-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.36.22840. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9278446
-
The polymorphism of acetylcholinesterase: post-translational processing, quaternary associations and localization.Chem Biol Interact. 1999 May 14;119-120:29-42. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(99)00011-3. Chem Biol Interact. 1999. PMID: 10421436 Review.
-
Tetramer-organizing polyproline-rich peptides differ in CHO cell-expressed and plasma-derived human butyrylcholinesterase tetramers.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jun;1864(6):706-714. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2016.03.003. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26947244
-
The origin of the molecular diversity and functional anchoring of cholinesterases.Neurosignals. 2002 May-Jun;11(3):130-43. doi: 10.1159/000065054. Neurosignals. 2002. PMID: 12138250 Review.
Cited by
-
Cryo-electron microscopy of cholinesterases, present and future.J Neurochem. 2021 Sep;158(6):1236-1243. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15245. Epub 2020 Dec 10. J Neurochem. 2021. PMID: 33222205 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anglister L, Silman I, Molecular structure of elongated forms of electric eel acetylcholinesterase, J Mol Biol, 125 (1978) 293–311. - PubMed
-
- Lee SL, Heinemann S, Taylor P, Structural characterization of the asymmetric (17 + 13) S forms of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo. I. Analysis of subunit composition, The Journal of biological chemistry, 257 (1982) 12282–12291. - PubMed
-
- Lee SL, Taylor P, Structural characterization of the asymmetric (17 + 13) S species of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo. II. Component peptides obtained by selective proteolysis and disulfide bond reduction, The Journal of biological chemistry, 257 (1982) 12292–12301. - PubMed
-
- Roberts WL, Doctor BP, Foster JD, Rosenberry TL, Bovine brain acetylcholinesterase primary sequence involved in intersubunit disulfide linkages, The Journal of biological chemistry, 266 (1991) 7481–7487. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberry TL, Richardson JM, Structure of 18S and 14S acetylcholinesterase. Identification of collagen-like subunits that are linked by disulfide bonds to catalytic subunits, Biochemistry, 16 (1977) 3550–3558. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

