Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis in Korean patients: clinico-radiologic-pathologic features and 2-year follow-up
- PMID: 32088939
- PMCID: PMC8009146
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2019.303
Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis in Korean patients: clinico-radiologic-pathologic features and 2-year follow-up
Abstract
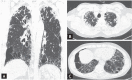
Background/aims: Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis (PPFE) is a type of rare idiopathic interstitial pneumonia that is characterized by predominantly upper lobe involvement with pleural fibrosis and subjacent parenchymal fibrosis. This study aimed to determine the clinico-radiologic-pathologic features and prognosis of Korean patients with PPFE.
Methods: A total of 26 patients who were confirmed to have PPFE by lung biopsy, were included, and their clinico-radiologic-pathologic findings were retrospectively analyzed.
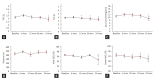
Results: The mean follow-up period was 23.8 months, and the mean age of the patients was 62.5 years; 61.5% were men and 50% were smokers. Cough and dyspnea were the most frequent presenting symptoms, and restrictive pattern was the most common observation in lung function. In 84.6% of the subjects, lower lobe involvement was found on chest computed tomography, and the usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) pattern was the most common (59.1%). Among patients whose lower lobe was biopsied (n = 13), the UIP pattern was the most common (46.2%). Patients with lower lobe involvement were older and walked a shorter distance during the 6-minute walk test, compared to those without. Spontaneous pneumothorax was a common complication (26.9%), and 15.4% of the patients died mostly due to pneumonia (100%). The 1- and 3-year survival rates were 90.2% and 84.5%, respectively.
Conclusion: Clinical features of Korean patients with PPFE were similar to those reported previously; however, lower lobe involvement was more frequent. During follow-up, one-fourth of the patients experienced pneumothorax and one-fifth died from pneumonia.
Keywords: Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias; Pleural diseases; Pulmonary fibrosis; Survival analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Frankel SK, Cool CD, Lynch DA, Brown KK. Idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis: description of a novel clinicopathologic entity. Chest. 2004;126:2007–2013. - PubMed
-
- Reddy TL, Tominaga M, Hansell DM, et al. Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis: a spectrum of histopathological and imaging phenotypes. Eur Respir J. 2012;40:377–385. - PubMed
-
- Nakatani T, Arai T, Kitaichi M, et al. Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis from a consecutive database: a rare disease entity? Eur Respir J. 2015;45:1183–1186. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe K, Nagata N, Kitasato Y, et al. Rapid decrease in forced vital capacity in patients with idiopathic pulmonary upper lobe fibrosis. Respir Investig. 2012;50:88–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
