Lumbar radiculopathy: Outcome analysis following treatment by only fixation - A report of an early experience of 44 cases
- PMID: 32089612
- PMCID: PMC7008660
- DOI: 10.4103/jcvjs.JCVJS_113_19
Lumbar radiculopathy: Outcome analysis following treatment by only fixation - A report of an early experience of 44 cases
Abstract
Objective: An alternative novel form of surgical treatment for patients having prolapsed or bulging intervertebral disc, with or without associated osteophyte, related lumbar radiculopathy by "only fixation" or internal orthosis and aiming for segmental arthrodesis is presented.
Materials and methods: During the period July 2014-October 2018, 44 patients presenting with symptoms of lumbar radiculopathy and diagnosed to have bulging, prolapsed or herniated lumbar intervertebral disc with or without associated osteophytes were treated by only spinal stabilization without resorting to any kind of bone, ligaments, osteophyte, or disc resection.
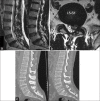
Results: All patients had "immediate" postoperative relief from radicular symptoms. The Visual Analog Scale and the Oswestry Disability Index scores were used to assess the patient both before and after the surgical treatment. During the follow-up period that ranged from 10 to 60 months (average: 35 months), there was no recurrence of symptoms. Complete or significant resorption of the herniated disc was seen in 29 cases on follow-up radiological assessment.
Conclusions: Spinal segmental fixation without any manipulation of the herniated disc or osteophyte and without any kind of bone or soft-tissue decompression is a safe, effective, and rational method of treatment of lumbar radiculopathy related to intervertebral disc herniation.
Keywords: Lumbar intervertebral disc; osteophyte; radiculopathy; spinal instability.
Copyright: © 2020 Journal of Craniovertebral Junction and Spine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Goel A, Dharurkar P, Shah A, Gore S, Bakale N, Vaja T. Facetal fixation arthrodesis as treatment of cervical radiculopathy. World Neurosurg. 2019;121:e875–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
