Tannase-Converted Green Tea Extract with High (-)-Epicatechin Inhibits Skeletal Muscle Mass in Aged Mice
- PMID: 32089721
- PMCID: PMC7008272
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/4319398
Tannase-Converted Green Tea Extract with High (-)-Epicatechin Inhibits Skeletal Muscle Mass in Aged Mice
Abstract
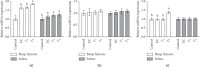
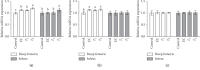
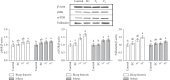
The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of tannase-converted green tea extract on body composition, muscle oxidative stress-related factors, and differentiation-related factors. The mean bone-related parameters and body composition were determined by the live dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and western blotting were used to determine mRNA expression and protein levels, respectively. The results of total mass testing in the epicatechin control (EC) and middle concentration tannase-converted green tea extract (T 1) intake groups were not significantly different compared with those in the control group; however, the high-concentration tannase-converted green tea extract (T 2) group showed a significantly higher effect to the lean than that of all other groups (p < 0.05). The results of the assay of muscle differentiation-related genes indicated that the expression levels in the EC and T 1 groups (p < 0.05) and the expression levels in the T 2 group (p < 0.01) were significantly different in the bicep femoris compared with that in the control group. The results of the SOD gene assay indicate that the expression levels in the EC and T 1 groups (p < 0.05) and the expression level in the T 2 group (p < 0.01) were significantly different in the bicep femoris compared with that in the control group. Additionally, SOD gene expression in the T 2 group was significantly increased (p < 0.05) in the soleus compared with that in the control, EC and T 1 groups. Our results suggest that tannase-converted green tea extract prevents muscle loss and regulates the quantity and quality of muscle by the levels of antioxidant stress-related enzymes and muscle differentiation factors to a greater extent than the administration of epicatechin and middle dose green tea extract.
Copyright © 2020 Ki-Bae Hong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
(-)-Epicatechin-Enriched Extract from Camellia sinensis Improves Regulation of Muscle Mass and Function: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jun 25;10(7):1026. doi: 10.3390/antiox10071026. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34202133 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of tannase-converted green tea extract on skeletal muscle development.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Feb 11;20(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-2827-7. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32046706 Free PMC article.
-
Tannase-converted green tea catechins and their anti-wrinkle activity in humans.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2013 Jun;12(2):137-43. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12038. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 23725307 Clinical Trial.
-
Physiological effects of formulation containing tannase-converted green tea extract on skin care: physical stability, collagenase, elastase, and tyrosinase activities.Integr Med Res. 2014 Mar;3(1):25-33. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2013.12.003. Epub 2013 Dec 14. Integr Med Res. 2014. PMID: 28664075 Free PMC article.
-
Improving the sweet aftertaste of green tea infusion with tannase.Food Chem. 2016 Feb 1;192:470-6. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.07.046. Epub 2015 Jul 10. Food Chem. 2016. PMID: 26304374
Cited by
-
Pathophysiological changes of muscle after ischemic stroke: a secondary consequence of stroke injury.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Apr;19(4):737-746. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.382221. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 37843207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutraceuticals in the Prevention and Treatment of the Muscle Atrophy.Nutrients. 2021 Jun 2;13(6):1914. doi: 10.3390/nu13061914. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34199575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
(-)-Epicatechin-Enriched Extract from Camellia sinensis Improves Regulation of Muscle Mass and Function: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jun 25;10(7):1026. doi: 10.3390/antiox10071026. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34202133 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Pathological Mechanisms and Natural Dietary Ingredients for the Management and Prevention of Sarcopenia.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 3;15(11):2625. doi: 10.3390/nu15112625. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37299588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Trends to Treat Muscular Atrophy: A Systematic Review of Epicatechin.Nutrients. 2024 Jan 22;16(2):326. doi: 10.3390/nu16020326. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38276564 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

