Development of a high affinity Anticalin® directed against human CD98hc for theranostic applications
- PMID: 32089738
- PMCID: PMC7019167
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.38968
Development of a high affinity Anticalin® directed against human CD98hc for theranostic applications
Abstract
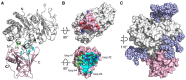
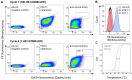
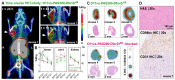
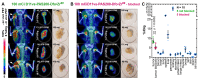
Enhanced amino acid supply and dysregulated integrin signaling constitute two hallmarks of cancer and are pivotal for metastatic transformation of cells. In line with its function at the crossroads of both processes, overexpression of CD98hc is clinically observed in various cancer malignancies, thus rendering it a promising tumor target. Methods: We describe the development of Anticalin proteins based on the lipocalin 2 (Lcn2) scaffold against the human CD98hc ectodomain (hCD98hcED) using directed evolution and protein design. X-ray structural analysis was performed to identify the epitope recognized by the lead Anticalin candidate. The Anticalin - with a tuned plasma half-life using PASylation® technology - was labeled with 89Zr and investigated by positron emission tomography (PET) of CD98-positive tumor xenograft mice. Results: The Anticalin P3D11 binds CD98hc with picomolar affinity and recognizes a protruding loop structure surrounded by several glycosylation sites within the solvent exposed membrane-distal part of the hCD98hcED. In vitro studies revealed specific binding activity of the Anticalin towards various CD98hc-expressing human tumor cell lines, suggesting broader applicability in cancer research. PET/CT imaging of mice bearing human prostate carcinoma xenografts using the optimized and 89Zr-labeled Anticalin demonstrated strong and specific tracer accumulation (8.6 ± 1.1 %ID/g) as well as a favorable tumor-to-blood ratio of 11.8. Conclusion: Our findings provide a first proof of concept to exploit CD98hc for non-invasive biomedical imaging. The novel Anticalin-based αhCD98hc radiopharmaceutical constitutes a promising tool for preclinical and, potentially, clinical applications in oncology.
Keywords: CD98hc; PASylation; cancer theranostics; lipocalin; protein engineering; tumor targeting.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: A.Sk. is cofounder and shareholder of Pieris Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and of XL-protein GmbH. M.S. has received a commercial research grant from Siemens Medical Solutions and has been acting as consultant for Siemens. W.W. serves on advisory boards and receives compensation from Bayer, Blue Earth Diagnostics, Endocyte and Pentixapharm; also, he has received research support from BMS, Imaginab, Ipsen and Piramal.
Figures

References
-
- Uhlén M, Fagerberg L, Hallstrom BM, Lindskog C, Oksvold P, Mardinoglu A. et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science. 2015;347:1260419. - PubMed
-
- Fotiadis D, Kanai Y, Palacin M. The SLC3 and SLC7 families of amino acid transporters. Mol Aspects Med. 2013;34:139–58. - PubMed
-
- Kanai Y, Segawa H, Miyamoto K, Uchino H, Takeda E, Endou H. Expression cloning and characterization of a transporter for large neutral amino acids activated by the heavy chain of 4F2 antigen (CD98) J Biol Chem. 1998;273:23629–32. - PubMed
-
- Pineda M, Fernandez E, Torrents D, Estevez R, Lopez C, Camps M. et al. Identification of a membrane protein, LAT-2, that co-expresses with 4F2 heavy chain, an L-type amino acid transport activity with broad specificity for small and large zwitterionic amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:19738–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

