Automatic Facial Paralysis Assessment via Computational Image Analysis
- PMID: 32089812
- PMCID: PMC7031725
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/2398542
Automatic Facial Paralysis Assessment via Computational Image Analysis
Abstract
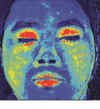
Facial paralysis (FP) is a loss of facial movement due to nerve damage. Most existing diagnosis systems of FP are subjective, e.g., the House-Brackmann (HB) grading system, which highly depends on the skilled clinicians and lacks an automatic quantitative assessment. In this paper, we propose an efficient yet objective facial paralysis assessment approach via automatic computational image analysis. First, the facial blood flow of FP patients is measured by the technique of laser speckle contrast imaging to generate both RGB color images and blood flow images. Second, with an improved segmentation approach, the patient's face is divided into concerned regions to extract facial blood flow distribution characteristics. Finally, three HB score classifiers are employed to quantify the severity of FP patients. The proposed method has been validated on 80 FP patients, and quantitative results demonstrate that our method, achieving an accuracy of 97.14%, outperforms the state-of-the-art systems. Experimental evaluations also show that the proposed approach could yield objective and quantitative FP diagnosis results, which agree with those obtained by an experienced clinician.
Copyright © 2020 Chaoqun Jiang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Neely J. G., Cherian N. G., Dickerson C. B., Nedzelski J. M. Sunnybrook facial grading system: reliability and criteria for grading. The Laryngoscope. 2010;120(5):1038–1045. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

