A Case Report with Severe Thrombocytopenia Induced by Axitinib
- PMID: 32089908
- PMCID: PMC7029294
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/7520783
A Case Report with Severe Thrombocytopenia Induced by Axitinib
Abstract
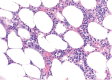
Axitinib is an oral, second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor that is selective for vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFR). This agent is approved as monotherapy or in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Axitinib is associated with a safety profile very similar to other anti-VEGFR inhibitors but usually with fewer hematologic adverse events, due to the selectivity for VEGF. In this report, we presented a rare case of grade 4 axitinib-induced thrombocytopenia, not observed with other antiangiogenic therapies. We discuss the differential diagnostic work-up, the necessary multidisciplinary approach, and the successful management of the case.
Copyright © 2020 Ulkuhan I. Koksal et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Hu-Lowe D. D., Zou H. Y., Grazzini M. L., et al. Nonclinical antiangiogenesis and antitumor activities of axitinib (AG-013736), an oral, potent, and selective inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases 1, 2, 3. Clinical Cancer Research. 2008;14(22):7272–7283. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-08-0652. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources