CYP2D6 polymorphism and its impact on the clinical response to metoprolol: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32090368
- PMCID: PMC7256128
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.14247
CYP2D6 polymorphism and its impact on the clinical response to metoprolol: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Aims: CYP2D6 genetic polymorphisms are associated with metoprolol pharmacokinetics. Whether the clinical response to metoprolol is also affected remains uncertain.
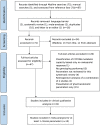
Methods: We conducted a systematic review on the effects of CYP2D6 polymorphism on the clinical response to metoprolol. Searches were conducted using MEDLINE. Meta-analyses were performed on the impact of CYP2D6-inferred phenotypes on heart rate (HR) reduction, diastolic (DBP) and systolic (SBP) blood pressure reduction, average daily doses, all-type adverse events and bradycardia.
Results: Our qualitative assessment indicated inconsistent results in individual studies and endpoints, but CYP2D6 poor metabolizers (PM) generally presented a greater reduction in HR. The meta-analysis of 15 studies, including a total of 1146 individuals, found a reduction in HR of 3 beats/min (P = .017), and of SBP and DBP by 3 mmHg (P = .0048) for PM compared to non-PM individuals using similar metoprolol doses. Bradycardia appeared more frequent by 4-fold for PM, although significant heterogeneity was observed regarding bradycardia, which limits the scope of this finding.
Conclusion: Patients without any CYP2D6 metabolic capacities appear to have increased reduction in DBP, HR and SBP during metoprolol treatment and may be at a higher risk of bradycardia compared to patients with active CYP2D6 phenotypes. Further prospective data are required to determine whether CYP2D6 is associated with clinical events in patients treated with metoprolol, as well as to demonstrate the clinical utility of an individualized approach of prescribing metoprolol using CYP2D6-inferred phenotypes.
Keywords: cytochrome P450 enzymes; genetic polymorphism; meta-analysis; pharmacogenomics; systematic review.
© 2020 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
M.‐P.D. is a coauthor on a patent pertaining to pharmacogenomics‐guided CETP inhibition and has minor equity interest in DalCor. M.‐P.D. has received honoraria from Dalcor and research support (access to samples and data) from AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Servier, Sanofi and GlaxoSmithKline. S.D. has received research support through grants from Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Roche Molecular Science, and DalCor.
Figures






References
-
- Zanger UM, Schwab M. Cytochrome P450 enzymes in drug metabolism: regulation of gene expression, enzyme activities, and impact of genetic variation. Pharmacol Ther. 2013;138(1):103‐141. - PubMed
-
- Swen JJ, Nijenhuis M, de Boer A, et al. Pharmacogenetics: from bench to byte‐‐an update of guidelines. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2011;89(5):662‐673. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

