Patterns of hypertension management in France in 2015: The ESTEBAN survey
- PMID: 32092238
- PMCID: PMC8029843
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.13834
Patterns of hypertension management in France in 2015: The ESTEBAN survey
Abstract
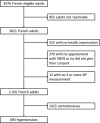
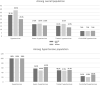
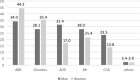
The purposes of this study were to describe the hypertensive population and therapeutic management of hypertension in adults between 18 and 74 years of age in France in 2015. Esteban survey is a cross-sectional survey with a clinical examination conducted in a representative sample of French adults aged 18-74 years between 2014 and 2016. Esteban was entirely public-funded. Blood pressure (BP) was measured during clinical examination with a standardized protocol, and pharmacological treatment was collected through the exhaustive Système National des Données de Santé (SNDS) database. Hypertension was defined by systolic BP (SBP)> 140 mm Hg, diastolic BP (DBP)> 90 mm Hg or treatment with BP-lowering drugs. The therapeutic control of treated hypertensive patients was defined by SBP < 140 mm Hg and DBP < 90 mm Hg. Adherence to drug treatment was defined as more than 80% of days covered by BP-lowering drug per year. The prevalence of hypertension was 31.3%. 74.7% of aware hypertensive participants taking an antihypertensive drug, and 57.7% of them were treated with a single antihypertensive pharmacological class. Overall, among hypertensives, 24.3% had a satisfactory BP control. Only 49.7% of treated hypertensives participants were controlled, and 33.6% of them were adherent to their drug treatment. The prevalence of hypertension in France remains high, with only 74.7% of the aware hypertensive participants receiving pharmacological therapy and only 48.9% of aware hypertensives with a BP at goal. More effective measures are needed to improve clinical management of hypertension in France.
Keywords: adherence; awareness; control; hypertension; therapy.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- WHO . A global brief on hypertension; 2013. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/79059/1/WHO_DCO_WHD_2013.2_eng.pdf
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet Lond Engl. 2005;365:217‐223. - PubMed
-
- Lawes CMM, Vander Hoorn S, Rodgers A, International Society of Hypertension . Global burden of blood‐pressure‐related disease, 2001. Lancet Lond Engl 2008;371:1513‐1518. - PubMed
-
- Wagner A, Dallongeville J, Ferrières J, Amouyel P, Haas B. État des lieux sur l’hypertension artérielle en France en 2007 : l’étude Mona Lisa. BEH. 2008; 49‐50.
-
- Godet‐Mardirossian H, Girerd X, Vernay M, Chamontin B, Castetbon K, de Peretti C. Patterns of hypertension management in France (ENNS 2006–2007). Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2012;19:213‐220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

