β2 Integrins-Multi-Functional Leukocyte Receptors in Health and Disease
- PMID: 32092981
- PMCID: PMC7073085
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21041402
β2 Integrins-Multi-Functional Leukocyte Receptors in Health and Disease
Abstract
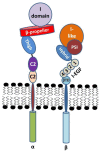
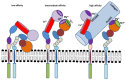
β2 integrins are heterodimeric surface receptors composed of a variable α (CD11a-CD11d) and a constant β (CD18) subunit and are specifically expressed by leukocytes. The α subunit defines the individual functional properties of the corresponding β2 integrin, but all β2 integrins show functional overlap. They mediate adhesion to other cells and to components of the extracellular matrix (ECM), orchestrate uptake of extracellular material like complement-opsonized pathogens, control cytoskeletal organization, and modulate cell signaling. This review aims to delineate the tremendous role of β2 integrins for immune functions as exemplified by the phenotype of LAD-I (leukocyte adhesion deficiency 1) patients that suffer from strong recurrent infections. These immune defects have been largely attributed to impaired migratory and phagocytic properties of polymorphonuclear granulocytes. The molecular base for this inherited disease is a functional impairment of β2 integrins due to mutations within the CD18 gene. LAD-I patients are also predisposed for autoimmune diseases. In agreement, polymorphisms within the CD11b gene have been associated with autoimmunity. Consequently, β2 integrins have received growing interest as targets in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Moreover, β2 integrin activity on leukocytes has been implicated in tumor development.
Keywords: LAD-I; LFA-1; MAC-1; autoimmune disease; cancer; infection; leukocytes; migration; phagocytosis; β2 integrin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

