A Systematic Review of the Effect of Dietary Supplements on Cognitive Performance in Healthy Young Adults and Military Personnel
- PMID: 32093203
- PMCID: PMC7071459
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12020545
A Systematic Review of the Effect of Dietary Supplements on Cognitive Performance in Healthy Young Adults and Military Personnel
Abstract
Intake of dietary supplements has increased, despite evidence that some of these have adverse side effects and uncertainty about their effectiveness. This systematic review examined the evidence for the cognitive benefits of a wide range of dietary supplements in healthy young adult samples; the aim was to identify if any might be useful for optimising cognitive performance during deployment in military personnel. Searches were conducted in 9 databases and 13 grey literature repositories for relevant studies published between January 2000 and June 2017. Eligible studies recruited healthy young adults (18-35 years), administered a legal dietary supplement, included a comparison control group, and assessed cognitive outcome(s). Thirty-seven of 394 identified studies met inclusion criteria and were included for synthesis. Most research was deemed of low quality (72.97%; SIGN50 guidelines), highlighting the need for sound empirical research in this area. Nonetheless, we suggest that tyrosine or caffeine could be used in healthy young adults in a military context to enhance cognitive performance when personnel are sleep-deprived. Caffeine also has the potential benefit of improving vigilance and attention during sustained operations offering little opportunity for sleep. Inconsistent findings and methodological limitations preclude firm recommendations about the use of other specific dietary supplements.
Keywords: cognition; cognitive performance enhancement; dietary supplements; healthy young adults; military.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no interests to declare. None of this work has been presented before in any journal; however, to fulfil Australian Army client reporting requirements, it has been summarised at the Defence Human Sciences Symposium, Adelaide, South Australia November 2017.
Figures
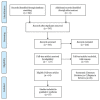
References
-
- Maughan R.J., Burke L.M., Dvorak J., Larson-Meyer D.E., Peeling P., Phillips S.M., Rawson E.S., Walsh N.P., Garthe I., Geyer H., et al. IOC consensus statement: dietary supplements and the high-performance athlete. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018;52:439–455. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2018-099027. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Knapik J.J., Trone D.W., Austin K.G., Steelman R.A., Farina E.K., Lieberman H.R. Prevalence, Adverse Events, and Factors Associated with Dietary Supplement and Nutritional Supplement Use by US Navy and Marine Corps Personnel. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016;116:1423–1442. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2016.02.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zion Market Research Dietary supplements market by ingredients (Botanicals, Vitamins, Minerals, Amino Acids, Enzymes) for additional supplements, medicinal supplements and sports nutrition applciations - Global industry perspective, Comprehensive analysis and forecast, 2016-2022. [(accessed on 23 June 2017)]; Available online: https://www.zionmarketresearch.com/report/dietary-supplements-market.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

