Essential newborn care utilization and associated factors in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32093648
- PMCID: PMC7041192
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-020-2804-7
Essential newborn care utilization and associated factors in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Globally, newborn death accounted for 46% of under-five deaths and more than 80% of newborn deaths are the result of preventable and treatable conditions. Findings on the prevalence and associated factors of essential newborn care utilization are highly variable and inconsistent across Ethiopia. Therefore, this systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to estimate the pooled prevalence of essential newborn care utilization and associated factors in Ethiopia.
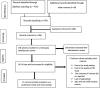
Methods: The international databases accessed included MEDLINE/PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Sciences, Scopus, and Grey literature databases, Google Scholar, Science Direct and Cochrane library were scientifically explored. We considered all primary studies reporting the prevalence of essential newborn care utilization and associated factors in Ethiopia. We retrieved all necessary data by using a standardized data extraction format spreadsheet. STATA 14 statistical software was used to analyze the data and Cochrane Q test statistics and I2 test was used to assess the heterogeneity between the studies. There significant heterogeneity between the studies so a random effect model was employed.
Results: The pooled estimate of essential newborn care utilization from 11 studies in Ethiopia was 48.77% (95% CI: 27.89, 69.65). Residence [OR = 2.50 (95% CI: 1.64, 3.88)], Postnatal care [OR = 5.53, 95% CI = (3.02, 10.13], counseling during pregnancy and delivery [OR = 4.39, 95% CI = (2.99, 6.45], antenatal care follows up (OR = 6.84; 95% CI: 1.15, 4.70) and maternal educational status [OR = 1.63 (95% CI: 1.12, 2.37)] were identified as associated factors of essential newborn care utilization.
Conclusion: Based on the current study essential newborn care utilization in Ethiopia was significantly low in comparison with the current global recommendation on essential newborn care utilization. Place of residence, Postnatal care, counseling during pregnancy and delivery, antenatal care follow up, and maternal educational status were associated risk factors. Therefore, on the basis of the results, it is suggested that special attention should be given to attempts to ensure that education should focus on women during ante and postnatal follow-up, counseling during pregnancy and delivery, as well as rural and illiterate mothers. Finally, appropriate newborn services at health facilities and raising mother's level of awareness about newborn care practices are imperative in addressing the gaps in essential newborn care utilization in Ethiopia.
Keywords: Ante/post-natal care; Essential newborn care utilization; Ethiopia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Continuum of maternal healthcare services utilization and its associated factors in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Womens Health (Lond). 2022 Jan-Dec;18:17455057221091732. doi: 10.1177/17455057221091732. Womens Health (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35412408 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of unemployment and post-natal care on the exclusive breast-feeding practice of women in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Reprod Health. 2022 Apr 15;19(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s12978-022-01404-y. Reprod Health. 2022. PMID: 35428313 Free PMC article.
-
Early Post-natal Care Services Utilization and its associated factors among mothers Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 18;10(1):e23760. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23760. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38192871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cervical cancer screening utilization and predictors among eligible women in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Nov 4;16(11):e0259339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259339. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34735507 Free PMC article.
-
Women's knowledge towards neonatal danger signs and its associated factors in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Pediatr. 2020 May 14;20(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s12887-020-02098-6. BMC Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32408874 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Home-based optimal newborn care practice and associated factors among mothers in Ethiopia: a community-based longitudinal panel survey.BMJ Open. 2023 Jul 10;13(7):e070999. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-070999. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 37429684 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of ANC follow up on essential newborn care practices in east Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 9;11(1):12210. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91821-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34108559 Free PMC article.
-
Geographic equity in essential newborn care practices in Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study.BMC Pediatr. 2025 Apr 9;25(1):281. doi: 10.1186/s12887-025-05645-1. BMC Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40205458 Free PMC article.
-
Geographical variation and predictors of missing essential newborn care items during the immediate postpartum period in Ethiopia: Spatial and multilevel count analyses.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 6;19(9):e0308104. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308104. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39240873 Free PMC article.
-
Healthcare providers' knowledge, attitude, and practice towards cervical cancer screening in Sub-Saharan Africa: systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 19;14:1436095. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1436095. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39224813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mohammadi Y, Parsaeian M, Farzadfar F, Kasaeian A, Mehdipour P, Sheidaei A, Mansouri A, Moghaddam SS, Djalalinia S, Mahmoudi M. Levels and trends of child and adult mortality rates in the Islamic Republic of Iran, 1990–2013; protocol of the NASBOD study. Arch Iran Med. 2014;17(3):176–181. - PubMed
-
- Jamison DT, Breman JG, Measham AR, Alleyne G, Claeson M, Evans DB, Jha P, Mills A, Musgrove P. Disease control priorities in developing countries: the World Bank. 2006. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad S, Goel K, Agarwal G, Goel P, Kumar V, Prakash A. Assessment of the newborn care practices in home deliveries among urban slums of Meerut, UP India. J Community Med Health Educ. 2012;2(171):2161–0711.1000171.
-
- Khan MH, Noman N, Hashmi G, Gul S, Ali A, Babar KS. Essential newborn care practice in the hospital versus home deliveries. Gomal J Med Sci. 2004;4(1):7-9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

