International evidence-based guidelines on Point of Care Ultrasound (POCUS) for critically ill neonates and children issued by the POCUS Working Group of the European Society of Paediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care (ESPNIC)
- PMID: 32093763
- PMCID: PMC7041196
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-020-2787-9
International evidence-based guidelines on Point of Care Ultrasound (POCUS) for critically ill neonates and children issued by the POCUS Working Group of the European Society of Paediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care (ESPNIC)
Abstract
Background: Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) is nowadays an essential tool in critical care. Its role seems more important in neonates and children where other monitoring techniques may be unavailable. POCUS Working Group of the European Society of Paediatric and Neonatal Intensive Care (ESPNIC) aimed to provide evidence-based clinical guidelines for the use of POCUS in critically ill neonates and children.
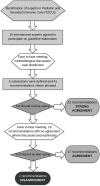
Methods: Creation of an international Euro-American panel of paediatric and neonatal intensivists expert in POCUS and systematic review of relevant literature. A literature search was performed, and the level of evidence was assessed according to a GRADE method. Recommendations were developed through discussions managed following a Quaker-based consensus technique and evaluating appropriateness using a modified blind RAND/UCLA voting method. AGREE statement was followed to prepare this document.
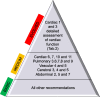
Results: Panellists agreed on 39 out of 41 recommendations for the use of cardiac, lung, vascular, cerebral and abdominal POCUS in critically ill neonates and children. Recommendations were mostly (28 out of 39) based on moderate quality of evidence (B and C).
Conclusions: Evidence-based guidelines for the use of POCUS in critically ill neonates and children are now available. They will be useful to optimise the use of POCUS, training programs and further research, which are urgently needed given the weak quality of evidence available.
Keywords: Children; Neonatal intensive care unit (NICU); Neonate; Paediatric intensive care unit (PICU); Point of care ultrasound (POCUS); Ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Towards use of POCUS to evaluate hemodynamics in critically ill neonates: caution before adoption in this population.Crit Care. 2021 Mar 3;25(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03394-4. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 33658049 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- On behalf of The Canadian Internal Medicine Ultrasound (CIMUS) Group*. Ma IWY, Arishenkoff S, Wiseman J, Desy J, Ailon J, et al. Internal Medicine Point-of-Care Ultrasound Curriculum: Consensus Recommendations from the Canadian Internal Medicine Ultrasound (CIMUS) Group. J Gen Intern Med. 2017;32:1052–1057. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Expert Round Table on Ultrasound in ICU International expert statement on training standards for critical care ultrasonography. Intensive Care Med. 2011;37:1077–1083. - PubMed
-
- Frankel HL, Kirkpatrick AW, Elbarbary M, Blaivas M, Desai H, Evans D, et al. Guidelines for the appropriate use of bedside general and cardiac ultrasonography in the evaluation of critically ill patients—part I: general ultrasonography. Crit Care Med. 2015;43:2479–2502. - PubMed
-
- Moore CL, Copel JA. Point-of-care ultrasonography. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:749–757. - PubMed
-
- Evans N, Gournay V, Cabanas F, Kluckow M, Leone T, Groves A, et al. Point-of-care ultrasound in the neonatal intensive care unit: international perspectives. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011;16:61–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical