Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio: A potential new peripheral biomarker of suicidal behavior
- PMID: 32093807
- PMCID: PMC7315873
- DOI: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2019.20
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio: A potential new peripheral biomarker of suicidal behavior
Abstract
Background: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (MLR), and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) have emerged as important peripheral inflammatory biomarkers. Recent data suggest a possible role of the immune system in the pathophysiology of suicidal behavior (SB). The aim of this study is to evaluate the association among NLR, MLR, and PLR and SB in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), and to test its validity as a biomarker for suicidality.
Methods: We evaluated 538 patients with MDD (mean age [standard deviation] = 43.87 [14.36] years; females: 68.8%). A logistic regression model was estimated to determine the independent factors associated with suicide risk in patients with and without a history of suicide attempt (SA).
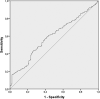
Results: Three hundred ninety-three patients (74.7%) had a personal history of SA. Patients with a previous SA were more frequently female (71.9% vs. 59.6%; p = 0.007), significantly younger (41.20 vs. 51.77 years; p < 0.001), had lower depression severity at enrolment (15.58 vs. 18.42; p < 0.000), and significantly higher mean NLR and PLR ratios (2.27 vs. 1.68, p = 0.001; 127.90 vs. 109.97, p = 0.007, respectively). In the final logistic regression model, after controlling for age, sex, and depression severity, NLR was significantly associated with SB (β = 0.489, p = 0.000; odds ratio [95% confidence intervals] = 1.631 [1.266-2.102]). We propose a cut-off value of NLR = 1.30 (sensitivity = 75% and specificity = 35%).
Conclusions: Our data suggest that NLR may be a valuable, reproducible, easily accessible, and cost-effective strategy to determine suicide risk in MDD.
Keywords: Major depressive disorder; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; suicide vulnerability; trait marker.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest relative to this study.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Public health action for prevention of suicide: a framework. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization Press; 2012.
-
- Blasco-Fontecilla H, Delgado-Gómez D, Ruiz-Hernández D, Aguado D, Baca-García E, López-Castroman J. Combining scales to assess suicide risk. J Psychiatr Res. 2012;46:1272–1277. - PubMed
-
- Hallensleben N, Glaesmer H, Forkmann T, Rath D, Strauss M, Kersting A, et al. Predicting suicidal ideation by interpersonal variables, hopelessness and depression in real-time. An ecological momentary assessment study in psychiatric inpatients with depression. Eur Psychiatry. 2019;56:43–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical