The antiviral compound remdesivir potently inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus
- PMID: 32094225
- PMCID: PMC7152756
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.AC120.013056
The antiviral compound remdesivir potently inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus
Abstract
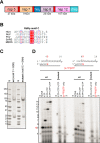
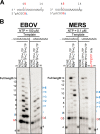
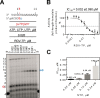
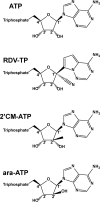
Antiviral drugs for managing infections with human coronaviruses are not yet approved, posing a serious challenge to current global efforts aimed at containing the outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (CoV-2). Remdesivir (RDV) is an investigational compound with a broad spectrum of antiviral activities against RNA viruses, including severe acute respiratory syndrome-CoV and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS-CoV). RDV is a nucleotide analog inhibitor of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRps). Here, we co-expressed the MERS-CoV nonstructural proteins nsp5, nsp7, nsp8, and nsp12 (RdRp) in insect cells as a part a polyprotein to study the mechanism of inhibition of MERS-CoV RdRp by RDV. We initially demonstrated that nsp8 and nsp12 form an active complex. The triphosphate form of the inhibitor (RDV-TP) competes with its natural counterpart ATP. Of note, the selectivity value for RDV-TP obtained here with a steady-state approach suggests that it is more efficiently incorporated than ATP and two other nucleotide analogs. Once incorporated at position i, the inhibitor caused RNA synthesis arrest at position i + 3. Hence, the likely mechanism of action is delayed RNA chain termination. The additional three nucleotides may protect the inhibitor from excision by the viral 3'-5' exonuclease activity. Together, these results help to explain the high potency of RDV against RNA viruses in cell-based assays.
Keywords: Ebola virus (EBOV); Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS–CoV); RNA chain termination; RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp); SARS–CoV-2; antiviral drug; coronavirus; drug development; enzyme inhibitor; nucleoside/nucleotide analog; plus-stranded RNA virus; positive-sense RNA virus; remdesivir; viral polymerase; viral replicase.
© 2020 Gordon et al.
Conflict of interest statement
M. G. has previously received funding from Gilead Sciences in support for the study of EBOV RdRp inhibition by RDV
Figures
References
-
- Sheahan T. P., Sims A. C., Leist S. R., Schäfer A., Won J., Brown A. J., Montgomery S. A., Hogg A., Babusis D., Clarke M. O., Spahn J. E., Bauer L., Sellers S., Porter D., Feng J. Y., et al. (2020) Comparative therapeutic efficacy of remdesivir and combination lopinavir, ritonavir, and interferon β against MERS–CoV. Nat. Commun. 11, 222 10.1038/s41467-019-13940-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Siegel D., Hui H. C., Doerffler E., Clarke M. O., Chun K., Zhang L., Neville S., Carra E., Lew W., Ross B., Wang Q., Wolfe L., Jordan R., Soloveva V., Knox J., et al. . (2017) Discovery and synthesis of a phosphoramidate prodrug of a pyrrolo[2,1-f][triazin-4-amino] adenine C-nucleoside (GS-5734) for the treatment of Ebola and emerging viruses. J. Med. Chem. 60, 1648–1661 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01594 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lo M. K., Jordan R., Arvey A., Sudhamsu J., Shrivastava-Ranjan P., Hotard A. L., Flint M., McMullan L. K., Siegel D., Clarke M. O., Mackman R. L., Hui H. C., Perron M., Ray A. S., Cihlar T., et al. (2017) GS-5734 and its parent nucleoside analog inhibit filo-, pneumo-, and paramyxoviruses. Sci. Rep. 7, 43395 10.1038/srep43395 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Warren T. K., Jordan R., Lo M. K., Ray A. S., Mackman R. L., Soloveva V., Siegel D., Perron M., Bannister R., Hui H. C., Larson N., Strickley R., Wells J., Stuthman K. S., Van Tongeren S. A., et al. . (2016) Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys. Nature 531, 381–385 10.1038/nature17180 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agostini M. L., Andres E. L., Sims A. C., Graham R. L., Sheahan T. P., Lu X., Smith E. C., Case J. B., Feng J. Y., Jordan R., Ray A. S., Cihlar T., Siegel D., Mackman R. L., Clarke M. O., et al. . (2018) Coronavirus susceptibility to the antiviral remdesivir (GS-5734) is mediated by the viral polymerase and the proofreading exoribonuclease. mBio 9, e00221–18 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

