Characterization and molecular epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus strains resistant to beta-lactams isolated from the milk of cows diagnosed with subclinical mastitis
- PMID: 32095043
- PMCID: PMC6989334
- DOI: 10.14202/vetworld.2019.1931-1939
Characterization and molecular epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus strains resistant to beta-lactams isolated from the milk of cows diagnosed with subclinical mastitis
Abstract
Background and aim: The term ESKAPE, recognized by the WHO, is an acronym, which refers to the pathogens Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter spp., which is extremely virulent and multidrug-resistant. Although the term is used to designate nosocomial pathogens, in a milking environment, strains of Methicillin-resistant S. aureus have been isolated from cattle diagnosed with clinical and subclinical mastitis. Resistant strains may be involved in the transfer of genes conferring resistance to beta-lactam antimicrobials among the species of microorganisms related to mastitis etiology. This study aimed to trace the phenotypic and genotypic profiles of susceptibility to beta-lactams in S. aureus isolated from milk of cattle diagnosed with subclinical mastitis obtained from different rural properties located in the North of Minas Gerais State, Brazil.
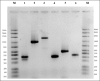
Materials and methods: Sixteen microorganisms previously identified as S. aureus isolated from milk of cattle diagnosed with subclinical mastitis were submitted to matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF), mass spectrometry, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis for microbial species confirmation. The S. aureus beta-lactams antimicrobial phenotypic resistance profile was investigated by disk diffusion method. PCR methods were also performed to investigate the S. aureus genotypic beta-lactams resistance profile. For this purpose, bla Z, mec A, mec ALGA251, bla Oxa23, and bla KPC genes were screened among S. aureus isolates. The genetic diversity of S. aureus by fingerprint random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD)-PCR was also performed in this study.
Results: All isolates showed phenotypic resistance to at least three beta-lactams, among which was meropenem. None of the isolates tested positive for the genes mec ALGA251, bla Oxa23, and bla KPC; however, the presence of the genes bla Z and mecA was detected among the isolates. The fingerprint analysis divided isolates into two distinct groups and 15 different subgroups. Despite the presence of clonality among the isolates, the PCR-RAPD analysis unveiled a heterogeneous profile with genetic diversity among the S. aureus isolates.
Conclusion: In this study, we identified beta-lactams resistant S. aureus strains isolated from the milk of cows diagnosed with subclinical mastitis. The S. aureus beta-lactams resistance was investigated using a phenotypic and genotypic approach. We believe that molecular epidemiology, improved knowledge, and genetic basis of resistance to beta-lactams might assist in asserting guidelines for better management practices of dealing with subclinical mastitis and mapping of origin of resistant pathogens in the studied Brazilian area.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; beta-lactams; genetic diversity; infection; resistance genes.
Copyright: © Souza, et al.
Figures

References
-
- Monistero V, Graber H.U, Pollera C, Cremonesi P, Castiglioni B, Bottini E, Ceballos-Marquez A, Lasso-Rojas L, Kroemker V, Wente N, Petzer I.M, Santisteban C, Runyan J, dos Santos M.V, Alves B.G, Piccinini R, Bronzo V, Abbassi M.S, Said M.B, Moroni P. Staphylococcus aureus isolates from bovine mastitis in eight countries:Genotypes, detection of genes encoding different toxins and other virulence genes. Toxins. 2018;10(6):2–22. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
