Tetrandrine Suppresses Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel Protein 6 Overexpression- Induced Podocyte Damage via Blockage of RhoA/ROCK1 Signaling
- PMID: 32095070
- PMCID: PMC6995298
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S234262
Tetrandrine Suppresses Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel Protein 6 Overexpression- Induced Podocyte Damage via Blockage of RhoA/ROCK1 Signaling
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Tetrandrine Suppresses Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel Protein 6 Overexpression- Induced Podocyte Damage via Blockage of RhoA/ROCK1 Signaling [Corrigendum].Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Mar 13;14:1143. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S252309. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32214799 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: Podocyte damage is common in many renal diseases characterized by proteinuria. Transient receptor potential cation channel protein 6 (TRPC6) plays an important role in renal function through its regulation of intracellular Ca2+ influx and RhoA/ROCK pathways. Chinese herb Stephania tetrandra, with the main active component being tetrandrine, has been used for the treatment of various kidney diseases for several years and has shown a positive effect. This study aimed at investigating the effect and mechanism of tetrandrine in podocyte damage induced by high expression of TRPC6.
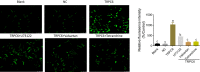
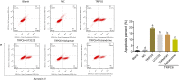
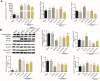
Methods: Immortalized, differentiated murine podocytes, MPC5 were treated with valsartan (0-800 μM) and tetrandrine (0-40 μM) for 48 h. The maximum safe concentrations of valsartan and tetrandrine were selected using a cell viability assay. MPC5 podocytes stably expressing TRPC6 were constructed using a lentivirus packaging system, followed by treatment with valsartan, tetrandrine, and Y-27632 for 48 h and U73122 (10 μM) for 10 min. The RhoA/ROCK pathway and podocyte-specific proteins (nephrin and synaptopodin) levels were quantified. Podocyte apoptosis and intracellular Ca2+ concentration were measured.
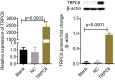
Results: Maximum safe concentrations of 100 μM valsartan and 10 μM tetrandrine showed no observable toxicity in podocytes. MPC5 podocytes stably expressing TRPC6 had higher intracellular Ca2+ influx, apoptotic percentages, and expression of RhoA/ROCK proteins, but lower expression of nephrin and synaptopodin proteins. U73122 treatment for 10 min did not inhibit TRPC6, but suppressed RhoA/ROCK protein. Y-27632 decreased ROCK1 expression, but did not influence the expression of TRPC6 protein. Both 100 μM valsartan and 10 μM tetrandrine for 48 h significantly inhibited intracellular Ca2+ influx, apoptosis, and RhoA/ROCK pathway, and increased nephrin and synaptopodin proteins in podocytes stably expressing TRPC6.
Conclusion: Elevated TRPC6 expression can lead to podocyte injury by inducing intracellular Ca2+ influx and apoptosis of podocytes, and this effect may be mediated by activation of the RhoA/ROCK1 pathway. Tetrandrine can alleviate podocyte injury induced by TRPC6 expression through inhibition of the RhoA/ROCK pathway, suggesting a protective role in podocyte damage.
Keywords: RhoA/ROCK pathway; podocyte; tetrandrine; transient receptor potential cation channel protein 6.
© 2020 Yu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

