Uric Acid and Arterial Stiffness
- PMID: 32095074
- PMCID: PMC6995306
- DOI: 10.2147/TCRM.S232033
Uric Acid and Arterial Stiffness
Abstract
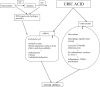
Hyperuricemia is usually associated with hypertension, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease. Accumulating data from epidemiological studies indicate an association of increased uric acid (UA) with cardiovascular diseases. Possible pathogenic mechanisms include enhancement of oxidative stress and systemic inflammation caused by hyperuricemia. Arterial stiffness may be one of the possible pathways between hyperuricemia and cardiovascular disease, but a clear relationship between increased UA and vascular alterations has not been confirmed. The review summarizes the epidemiological studies investigating the relationship between UA and arterial stiffness and highlights the results of interventional studies evaluating arterial stiffness parameters in patients treated with UA-lowering drugs.
Keywords: arterial stiffness; cardiovascular risk; uric acid.
© 2020 Albu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Wang JG, Staessen JA. Raised concentrations of serum creatinine and uric acid and the risks of mortality and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Rev Rep. 2002;23:393–399.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources