miR-214-3p Regulates Multi-Drug Resistance and Apoptosis in Retinoblastoma Cells by Targeting ABCB1 and XIAP
- PMID: 32095078
- PMCID: PMC6995305
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S235862
miR-214-3p Regulates Multi-Drug Resistance and Apoptosis in Retinoblastoma Cells by Targeting ABCB1 and XIAP
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been shown to contribute to the initiation and progression of human cancer, including retinoblastoma. However, expression levels and potential roles of miRNAs in retinoblastoma remain largely unknown. In this study, we aimed to identify dysregulated miRNAs and explore their functional roles in the development of retinoblastoma.
Material and methods: First, miRNA expression profiling in retinoblastoma tissues was performed via microarray analysis. To evaluate the involvement of miR-214-3p in multi-drug resistance, gain-of-function experiments were employed in vitro and in vivo. Bioinformatics analysis, luciferase reporter assay, qRT-PCR and Western blot were used to investigate the underlying mechanisms.
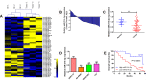
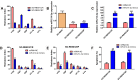
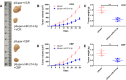
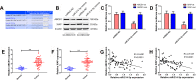
Results: Here, we identified 57 up-regulated and 34 down-regulated miRNAs. Among them, miR-214-3p was the most significantly decreased. We found that miR-214-3p level was positively correlated with clinical outcome and chemotherapy response. Overexpression of miR-214-3p significantly sensitized retinoblastoma cells to multiple chemodrugs and promoted cell apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Further investigations revealed that miR-214-3p directly regulated ABCB1 and XIAP expression through interacting with the 3' untranslated regions (3'UTRs). Pearson correlation analysis showed that miR-214-3p expression in retinoblastoma tissues was negatively correlated with ABCB1 and XIAP expression. We also observed that overexpression of ABCB1 or XIAP partly reversed the chemoresistance inhibition-induced by miR-214-3p overexpression.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrate that miR-214-3p functions as a tumor suppressor to inhibit the chemoresistance in retinoblastoma, suggesting that miR-214-3p might be potential diagnostic and therapeutic targets for retinoblastoma treatment.
Keywords: ABCB1; XIAP; chemoresistance; miR-214-3p; retinoblastoma.
© 2020 Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-141-3p promotes retinoblastoma progression via inhibiting sushi domain-containing protein 2.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):7410-7424. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2048770. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35259051 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of microRNA-224-3p Hampers Retinoblastoma Progression via Activation of the Hippo-YAP Signaling Pathway by Increasing LATS2.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Mar 9;61(3):32. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.3.32. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32186675 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA -378a-3p Restrains the Proliferation of Retinoblastoma Cells but Promotes Apoptosis of Retinoblastoma Cells via Inhibition of FOXG1.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 May 11;61(5):31. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.5.31. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32428232 Free PMC article.
-
miR-142-5p enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells by targeting multiple anti-apoptotic genes.Biochem Pharmacol. 2019 Mar;161:98-112. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.01.009. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30639456
-
Long non-coding RNA ROR regulated ABCB1 to induce cisplatin resistance in osteosarcoma by sponging miR-153-3p.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Sep;23(17):7256-7265. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201909_18828. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31539112
Cited by
-
Role of Epigenetics for the Efficacy of Cisplatin.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 17;25(2):1130. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021130. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Mechanisms of Chemoresistance in Retinoblastoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 10;14(19):4966. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194966. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230889 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA POLR2J4 Plays a Biomarker Role in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through Regulating miR-214-3p.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2024 Aug 26;35(10):787-794. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2024.24150. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39412398 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles derived from paclitaxel-sensitive nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells deliver miR-183-5p and impart paclitaxel sensitivity through a mechanism involving P-gp.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023 Dec;39(6):2953-2970. doi: 10.1007/s10565-023-09812-x. Epub 2023 Jun 10. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37296288
-
Effect of miR-515-5p on Proliferation and Drug Sensitivity of Retinoblastoma Cells.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Nov 24;12:12087-12098. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S271165. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 33262657 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

