Dynamic Changes in Serum Markers and Their Utility in the Early Diagnosis of All Stages of Hepatitis B-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 32095079
- PMCID: PMC6995291
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S229835
Dynamic Changes in Serum Markers and Their Utility in the Early Diagnosis of All Stages of Hepatitis B-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the individual and combined diagnostic values of serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), des-gamma-carboxyprothrombin (DCP), glypican-3 (GPC3) and golgi protein 73 (GP73) in diagnosing hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods: Participants from Beijing YouAn Hospital were enrolled and divided into seven groups. Serum was collected and the levels of AFP, GPC3, GP73 and DCP were simultaneously measured with a protein array. Pearson's χ2 test was applied to compare the clinicopathological characteristics. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to analyse the diagnostic performance of the four markers.
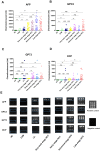
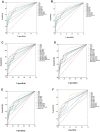
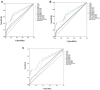
Results: As a single biomarker for differentiating HCC from all controls, AFP had a larger area under the curve (AUC) (0.798, 95% CI (0.754-0.838) than the other biomarkers, with a sensitivity of 77.3% and a specificity of 71.1%. Among the other combinations, AFP plus GPC3 and DCP (0.871, 95% CI (0.833-0.903)) was the best at differentiating HCC from all controls. In discriminating very early stage and early stage HCC from all controls, the AUC of GPC3 (0.744, 95% CI (0.690-0.793); sensitivity 62.8%; specificity 83.3%) was better than that of AFP (0.723, 95% CI (0.668-0.774); sensitivity 67.3%; specificity 71.7%). Among all biomarker combinations, the combination of AFP, GPC3 and GP73 had the largest AUC (0.843, 95% CI (0.796-0.883); sensitivity 84.1%; specificity 71.7%). AFP (AUC 0.726, 95% CI (0.662-0.784)) showed the best performance in the very early diagnosis of HBV-related HCC.
Conclusion: As a single biomarker, AFP has an advantage in the very early and early diagnosis of HBV-related HCC. The combination of AFP, GPC3 and GP73 is the most suitable marker for the early diagnosis of HBV-related HCC. However, AFP remains the best biomarker for the very early diagnosis of HBV-related HCC, and the adding of one or more markers does not significantly improve the diagnostic accuracy.
Keywords: diagnosis; hepatitis B virus; hepatocellular carcinoma; protein array.
© 2020 Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Freddie B, Jacques F, Isabelle S, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A, Clinicians JAJCACJf. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2015. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;60(5):277–300. - PubMed
-
- Chen CJ, Liang K-Y, Chang A-S, et al. Effects of hepatitis B virus, alcohol drinking, cigarette smoking and familial tendency on hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1991;13(3):398–406. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

