Advances in the chemistry, pharmacological diversity, and metabolism of 20(R)-ginseng saponins
- PMID: 32095093
- PMCID: PMC7033361
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2019.01.005
Advances in the chemistry, pharmacological diversity, and metabolism of 20(R)-ginseng saponins
Abstract
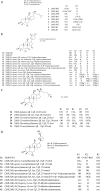
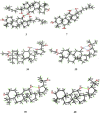
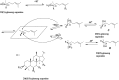
Ginseng has been used as a popular herbal medicine in East Asia for at least two millennia. However, 20(R)-ginseng saponins, one class of important rare ginsenosides, are rare in natural products. 20(R)-ginseng saponins are generally prepared by chemical epimerization and microbial transformation from 20(S)-isomers. The C20 configuration of 20(R)-ginseng saponins are usually determined by 13C NMR and X-ray single-crystal diffraction. 20(R)-ginseng saponins have antitumor, antioxidative, antifatigue, neuroprotective, and osteoclastogenesis inhibitory effects, among others. Owing to the chemical structure and pharmacological and stereoselective properties, 20(R)-ginseng saponins have attracted a great deal of attention in recent years. In this study, the discovery, identification, chemical epimerization, microbial transformation, pharmacological activities, and metabolism of 20(R)-ginseng saponins are summarized.
Keywords: 20(R)-ginseng saponin; Epimerization; Identification; Metabolism; Pharmacological activity.
© 2019 The Korean Society of Ginseng. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stereoscopic Differences in the Identification, Bioactivity, and Metabolism of C-20 and C-24 Epimeric Ginseng Saponins.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2023;23(7):804-820. doi: 10.2174/1389557522666221012095258. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36237162
-
Research progress on chemical diversity of saponins in Panax ginseng.Chin Herb Med. 2024 Sep 3;16(4):529-547. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2024.08.005. eCollection 2024 Oct. Chin Herb Med. 2024. PMID: 39606259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery, semisynthesis, biological activities, and metabolism of ocotillol-type saponins.J Ginseng Res. 2017 Jul;41(3):373-378. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2017.01.001. Epub 2017 Jan 13. J Ginseng Res. 2017. PMID: 28701880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Saponins of ginseng products: a review of their transformation in processing.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 28;14:1177819. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1177819. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37188270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Saponin Diversity of Panax ginseng.Molecules. 2020 Jul 29;25(15):3452. doi: 10.3390/molecules25153452. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32751233 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rare ginsenosides: A unique perspective of ginseng research.J Adv Res. 2024 Dec;66:303-328. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.01.003. Epub 2024 Jan 7. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 38195040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cerium-Promoted Ginsenosides Accumulation by Regulating Endogenous Methyl Jasmonate Biosynthesis in Hairy Roots of Panax ginseng.Molecules. 2021 Sep 16;26(18):5623. doi: 10.3390/molecules26185623. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34577094 Free PMC article.
-
UPLC-TOF/MS-based metabolomics reveals the chemical changes and in vitro biological effects in fermentation of white ginseng by four probiotics.Front Microbiol. 2022 Nov 24;13:1022200. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1022200. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36504795 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of Korean Red Ginseng against toxicity of endocrine-disrupting chemicals.J Ginseng Res. 2023 Mar;47(2):193-198. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2022.11.007. Epub 2022 Dec 5. J Ginseng Res. 2023. PMID: 36926605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can Panax ginseng help control cytokine storm in COVID-19?J Ginseng Res. 2022 May;46(3):337-347. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2022.02.006. Epub 2022 Feb 25. J Ginseng Res. 2022. PMID: 35233163 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Garriques S.S. On panaquilon, a new vegetable substance. Ann Chem Pharm. 1854;90:231–234.
-
- Shibata S., Tanaka O., NagaI M., Ishit T. Studies on the constituents of Japanese and Chinese crude drugs. XII. Panaxadiol, a sapogenin of ginseng roots. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1963;11:762–765. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

