Macrophase-Separated Organic Ionic Plastic Crystals/PAMPS-Based Ionomer Electrolyte: A New Design Perspective for Flexible and Highly Conductive Solid-State Electrolytes
- PMID: 32095715
- PMCID: PMC7033988
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.9b03773
Macrophase-Separated Organic Ionic Plastic Crystals/PAMPS-Based Ionomer Electrolyte: A New Design Perspective for Flexible and Highly Conductive Solid-State Electrolytes
Abstract
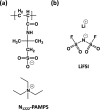
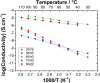
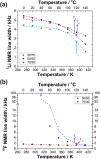
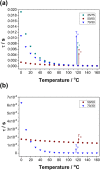
A material design approach was taken for the preparation of an organic ionic plastic crystal (OIPC)-polymer electrolyte material that exhibited both good mechanical and transport properties. Previous attempts to form this type of electrolyte material resulted in the solvation of the OIPC by the ionomer and loss of the plastic crystal component. Here, we prepared, in situ, a macrophase-separated OIPC-polymer electrolyte system by adding lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (LiFSI) to a (PAMPS-N1222) ionomer. It was found that an optimal compositional window of 40-50 mol % LiFSI exists whereby the electrolyte conductivity suddenly increased 4 orders of magnitude while exhibiting elastic and flexible mechanical properties. The phase behavior and transport properties were studied using differential scanning calorimetry and 7Li and 19F solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. This is the first example of a fabrication principle that lends itself to a wide range of promising OIPC and ionomeric materials. Subsequent studies are required to characterize and understand the morphology and conductive nature of these systems and their application as electrolyte materials.
Copyright © 2020 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Howlett P. C.; Brack N.; Hollenkamp A. F.; Forsyth M.; MacFarlane D. R. Characterization of the Lithium Surface in N-Methyl-N-Alkylpyrrolidinium Bis(Trifluoromethanesulfonyl)Amide Room-Temperature Ionic Liquid Electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, A595–A606. 10.1149/1.2164726. - DOI
-
- Forsyth M.; Girard G. M. A.; Basile A.; Hilder M.; MacFarlane D. R.; Chen F.; Howlett P. C. Inorganic-Organic Ionic Liquid Electrolytes Enabling High Energy-Density Metal Electrodes for Energy Storage. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 220, 609–617. 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.10.134. - DOI
-
- Monroe C.; Newman J. The Impact of Elastic Deformation on Deposition Kinetics at Lithium/Polymer Interfaces. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A396–A404. 10.1149/1.1850854. - DOI
-
- Stone G. M.; Mullin S. A.; Teran A. A.; Hallinan D. T.; Minor A. M.; Hexemer A.; Balsara N. P. Resolution of the Modulus versus Adhesion Dilemma in Solid Polymer Electrolytes for Rechargeable Lithium Metal Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, A222–A227. 10.1149/2.030203jes. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
