TBCRC 031: Randomized Phase II Study of Neoadjuvant Cisplatin Versus Doxorubicin-Cyclophosphamide in Germline BRCA Carriers With HER2-Negative Breast Cancer (the INFORM trial)
- PMID: 32097092
- PMCID: PMC8462533
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.19.03292
TBCRC 031: Randomized Phase II Study of Neoadjuvant Cisplatin Versus Doxorubicin-Cyclophosphamide in Germline BRCA Carriers With HER2-Negative Breast Cancer (the INFORM trial)
Abstract
Purpose: Platinum compounds have activity in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) in germline BRCA mutation carriers (BRCA carriers). Limited data exist for estrogen receptor (ER)-positive (+) breast cancer among BRCA carriers. INFORM is a randomized, multicenter, phase II trial comparing pathologic complete response (pCR) rates (ypT0/is, N0) after neoadjuvant single-agent cisplatin (CDDP) versus doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide (AC) in BRCA carriers with stage I-III human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative breast cancer. Secondary objectives included residual cancer burden scores (RCB) of 0 or 1 (combined) and toxicity. The goal was to determine whether pCR was ≥ 20% higher with CDDP than AC.
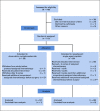
Patients and methods: BRCA carriers with cT1-3 (≥ 1.5 cm), cN0-3 HER2-negative breast cancer were randomly assigned to preoperative CDDP (75 mg/m2 every 3 weeks × 4 doses) or AC (doxorubicin 60 mg/m2; cyclophosphamide 600 mg/m2 every 2-3 weeks × 4 doses) followed by surgery. Pathologic responses were confirmed by central review.
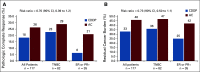
Results: A total of 118 patients were randomly assigned; 117 were included in outcome analyses. Mean age was 42 years (range, 24-73 years); 69% were BRCA1+, 30% were BRCA2+, and 2% had both mutations. Clinical stage was I for 19%, II for 63%, and III for 18%; 45% had nodal involvement at baseline. Seventy percent had TNBC. Clinical and tumor characteristics were well matched between treatment arms. The pCR rate was 18% with CDDP and 26% with AC, yielding a risk ratio (RR) of 0.70 (90% CI, 0.39 to 1.2). The risk of RCB 0 or 1 (RCB 0/1) was 33% with CDDP and 46% with AC (RR, 0.73; 90% CI, 0.50 to 1.1). Both regimens were generally well tolerated without unexpected toxicities.
Conclusion: pCR or RCB 0/1 is not significantly higher with CDDP than with AC in BRCA carriers with stage I-III HER2-negative breast cancer for both TNBC and ER+/HER2-negative disease.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01670500.
Conflict of interest statement
TBCRC 031: Randomized Phase II Study of Neoadjuvant Cisplatin Versus Doxorubicin-Cyclophosphamide in Germline
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Nadine Tung
Banu Arun
Erin Hofstatter
Deborah L. Toppmeyer
Steven J. Isakoff
Virginia Borges
Robert D. Legare
Claudine Isaacs
Antonio C. Wolff
Paul Kelly Marcom
Erica L. Mayer
Ian E. Krop
Eric P. Winer
Judy E. Garber
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures


Comment in
-
Reply to S. Takamizawa et al.J Clin Oncol. 2020 Aug 10;38(23):2700-2701. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.01190. Epub 2020 Jun 9. J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32516090 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Neoadjuvant Cisplatin in BRCA Carriers With HER2-Negative Breast Cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2020 Aug 10;38(23):2699-2700. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.00789. Epub 2020 Jun 9. J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32516091 No abstract available.
References
-
- Byrski T, Huzarski T, Dent R, et al. Pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant cisplatin in BRCA1-positive breast cancer patients Breast Cancer Res Treat 147401–4052014 - PubMed
-
- Byrski T, Gronwald J, Huzarski T, et al. Pathologic complete response rates in young women with BRCA1-positive breast cancers after neoadjuvant chemotherapy J Clin Oncol 28375–3792010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

