High-Throughput Proteomics Enabled by a Photocleavable Surfactant
- PMID: 32097521
- PMCID: PMC7230032
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201915374
High-Throughput Proteomics Enabled by a Photocleavable Surfactant
Abstract
Mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics provides unprecedented opportunities for understanding the structure and function of proteins in complex biological systems; however, protein solubility and sample preparation before MS remain a bottleneck preventing high-throughput proteomics. Herein, we report a high-throughput bottom-up proteomic method enabled by a newly developed MS-compatible photocleavable surfactant, 4-hexylphenylazosulfonate (Azo) that facilitates robust protein extraction, rapid enzymatic digestion (30 min compared to overnight), and subsequent MS-analysis following UV degradation. Moreover, we developed an Azo-aided bottom-up method for analysis of integral membrane proteins, which are key drug targets and are generally underrepresented in global proteomic studies. Furthermore, we demonstrated the ability of Azo to serve as an "all-in-one" MS-compatible surfactant for both top-down and bottom-up proteomics, with streamlined workflows for high-throughput proteomics amenable to clinical applications.
Keywords: high-throughput proteomics; mass spectrometry; membrane proteins; photocleavable surfactants.
© 2020 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

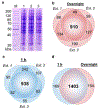
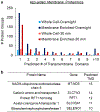
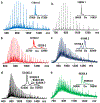

References
-
- Hopper JTS, Robinson CV, Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2014, 53, 14002–14015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

