Favipiravir, an anti-influenza drug against life-threatening RNA virus infections
- PMID: 32097670
- PMCID: PMC7102570
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107512
Favipiravir, an anti-influenza drug against life-threatening RNA virus infections
Abstract
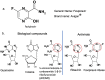
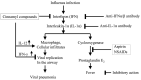
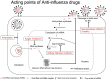
Favipiravir has been developed as an anti-influenza drug and licensed as an anti-influenza drug in Japan. Additionally, favipiravir is being stockpiled for 2 million people as a countermeasure for novel influenza strains. This drug functions as a chain terminator at the site of incorporation of the viral RNA and reduces the viral load. Favipiravir cures all mice in a lethal influenza infection model, while oseltamivir fails to cure the animals. Thus, favipiravir contributes to curing animals with lethal infection. In addition to influenza, favipiravir has a broad spectrum of anti-RNA virus activities in vitro and efficacies in animal models with lethal RNA viruses and has been used for treatment of human infection with life-threatening Ebola virus, Lassa virus, rabies, and severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. The best feature of favipiravir as an antiviral agent is the apparent lack of generation of favipiravir-resistant viruses. Favipiravir alone maintains its therapeutic efficacy from the first to the last patient in an influenza pandemic or an epidemic lethal RNA virus infection. Favipiravir is expected to be an important therapeutic agent for severe influenza, the next pandemic influenza strain, and other severe RNA virus infections for which standard treatments are not available.
Keywords: Antiviral agent; Chain termination; Ebola; Favipiravir; Influenza; Resistant virus.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest K.S. reports the receipt of consulting fees from Maruho Co., Ltd., lecture fees from Maruho Co., Ltd., MSD, and Novartis, and research funding from Maruho Co., Ltd., MSD, and Japan Blood Products Organization; all payments were sent to the institution.
Figures


References
-
- Abdelnabi R., Jochmans D., Verbeken E., Neyts J., Delang L. Antiviral treatment efficiently inhibits chikungunya virus infection in the joints of mice during the acute but not during the chronic phase of the infection. Antiviral Research. 2018;149:113–117. - PubMed
-
- Akahoshi Y., Kanda J., Ohno A., Komiya Y., Gomyo A., Hayakawa J.…Kanda Y. Acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus 1 infection early after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with T-cell depletion. Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy. 2017;23:485–487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

