Complement factor I deficiency: A potentially treatable cause of fulminant cerebral inflammation
- PMID: 32098865
- PMCID: PMC7051217
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000689
Complement factor I deficiency: A potentially treatable cause of fulminant cerebral inflammation
Abstract
Objective: To raise awareness of complement factor I (CFI) deficiency as a potentially treatable cause of severe cerebral inflammation.
Methods: Case report with neuroradiology, neuropathology, and functional data describing the mutation with review of literature.
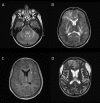
Results: We present a case of acute, fulminant, destructive cerebral edema in a previously well 11-year-old, demonstrating massive activation of complement pathways on neuropathology and compound heterozygote status for 2 pathogenic mutations in CFI which result in normal levels but completely abrogate function.
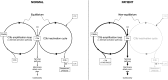
Conclusions: Our case adds to a very small number of extant reports of this phenomenon associated with a spectrum of inflammatory histopathologies including hemorrhagic leukoencephalopathy and clinical presentations resembling severe acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. CFI deficiency can result in uncontrolled activation of the complement pathways in the brain resulting in devastating cerebral inflammation. The deficit is latent, but the catastrophic dysregulation of the complement system may be the result of a C3 acute phase response. Diagnoses to date have been retrospective. Diagnosis requires a high index of suspicion and clinician awareness of the limitations of first-line clinical tests of complement activity and activation. Simple measurement of circulating CFI levels, as here, may fail to diagnose functional deficiency with absent CFI activity. These diagnostic challenges may mean that the CFI deficiency is being systematically under-recognized as a cause of fulminant cerebral inflammation. Complement inhibitory therapies (such as eculizumab) offer new potential treatment, underlining the importance of prompt recognition, and real-time whole exome sequencing may play an important future role.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures

References
-
- Nilsson SC, Sim RB, Lea SM, Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Blom AM. Complement factor I in health and disease. Mol Immunol 2011;48:1611–1620. - PubMed
-
- Kavanagh D, Kemp EJ, Mayland E, et al. . Mutations in complement factor I predispose to development of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005;16:2150–2155. - PubMed
-
- Hakobyan S, Harding K, Aiyaz M, et al. . Complement biomarkers as predictors of disease progression in alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2016;54:707–716. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
