ROCK/PKA Inhibition Rescues Hippocampal Hyperexcitability and GABAergic Neuron Alterations in a Oligophrenin-1 Knock-Out Mouse Model of X-Linked Intellectual Disability
- PMID: 32098904
- PMCID: PMC7096135
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0462-19.2020
ROCK/PKA Inhibition Rescues Hippocampal Hyperexcitability and GABAergic Neuron Alterations in a Oligophrenin-1 Knock-Out Mouse Model of X-Linked Intellectual Disability
Abstract
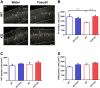
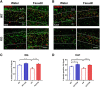
Oligophrenin-1 (Ophn1) encodes a Rho GTPase activating protein whose mutations cause X-linked intellectual disability (XLID) in humans. Loss of function of Ophn1 leads to impairments in the maturation and function of excitatory and inhibitory synapses, causing deficits in synaptic structure, function and plasticity. Epilepsy is a frequent comorbidity in patients with Ophn1-dependent XLID, but the cellular bases of hyperexcitability are poorly understood. Here we report that male mice knock-out (KO) for Ophn1 display hippocampal epileptiform alterations, which are associated with changes in parvalbumin-, somatostatin- and neuropeptide Y-positive interneurons. Because loss of function of Ophn1 is related to enhanced activity of Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) and protein kinase A (PKA), we attempted to rescue Ophn1-dependent pathological phenotypes by treatment with the ROCK/PKA inhibitor fasudil. While acute administration of fasudil had no impact on seizure activity, seven weeks of treatment in adulthood were able to correct electrographic, neuroanatomical and synaptic alterations of Ophn1 deficient mice. These data demonstrate that hyperexcitability and the associated changes in GABAergic markers can be rescued at the adult stage in Ophn1-dependent XLID through ROCK/PKA inhibition.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT In this study we demonstrate enhanced seizure propensity and impairments in hippocampal GABAergic circuitry in Ophn1 mouse model of X-linked intellectual disability (XLID). Importantly, the enhanced susceptibility to seizures, accompanied by an alteration of GABAergic markers were rescued by Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK)/protein kinase A (PKA) inhibitor fasudil, a drug already tested on humans. Because seizures can significantly impact the quality of life of XLID patients, the present data suggest a potential therapeutic pathway to correct alterations in GABAergic networks and dampen pathological hyperexcitability in adults with XLID.
Keywords: GABAergic interneurons; electrographic seizures; epilepsy; fasudil; inhibitory synapses.
Copyright © 2020 the authors.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Pharmacological rescue of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in a mouse model of X-linked intellectual disability.Neurobiol Dis. 2017 Apr;100:75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2017.01.003. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Neurobiol Dis. 2017. PMID: 28088401 Free PMC article.
-
Rho Kinase Inhibition Is Essential During In Vitro Neurogenesis and Promotes Phenotypic Rescue of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neurons With Oligophrenin-1 Loss of Function.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016 Jul;5(7):860-9. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0303. Epub 2016 May 9. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27160703 Free PMC article.
-
Fasudil treatment in adult reverses behavioural changes and brain ventricular enlargement in Oligophrenin-1 mouse model of intellectual disability.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Jun 1;25(11):2314-2323. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw102. Epub 2016 May 4. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 27146843
-
Expanding the phenotypic spectrum associated with OPHN1 mutations: Report of 17 individuals with intellectual disability but no cerebellar hypoplasia.Eur J Med Genet. 2018 Aug;61(8):442-450. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2018.03.002. Epub 2018 Mar 3. Eur J Med Genet. 2018. PMID: 29510240 Review.
-
Evaluation of clinical efficacy of fasudil for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov. 2012 Aug;7(2):100-4. doi: 10.2174/157489012801227238. Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov. 2012. PMID: 22670803 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuronal Cytoskeleton in Intellectual Disability: From Systems Biology and Modeling to Therapeutic Opportunities.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 7;22(11):6167. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116167. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34200511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Rho-associated kinases and their inhibitor fasudil in neurodegenerative diseases.Front Neurosci. 2024 Nov 19;18:1481983. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1481983. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39628659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent updates on novel therapeutic targets of cardiovascular diseases.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Jan;476(1):145-155. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03891-8. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 32845435 Review.
-
Hippocampal Excitatory Synaptic Transmission and Plasticity Are Differentially Altered during Postnatal Development by Loss of the X-Linked Intellectual Disability Protein Oligophrenin-1.Cells. 2022 May 5;11(9):1545. doi: 10.3390/cells11091545. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563851 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Rho/ROCK in epileptic seizure-related neuronal damage.Metab Brain Dis. 2022 Apr;37(4):881-887. doi: 10.1007/s11011-022-00909-6. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Metab Brain Dis. 2022. PMID: 35119588 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
