Corneal confocal microscopy detects small nerve fibre damage in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy
- PMID: 32099076
- PMCID: PMC7042367
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-60422-7
Corneal confocal microscopy detects small nerve fibre damage in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy
Abstract
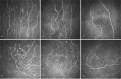
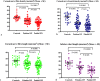
Neuropathic pain is believed to arise from damage to nociceptive C fibres in diabetic neuropathy (DN). We have utilised corneal confocal microscopy (CCM) to quantify the severity of small nerve fibre damage in relation to the severity of neuropathic pain and quality of life (QoL) in patients with and without painful DN. 30 controls and patients with painful (n = 78) and painless (n = 62) DN underwent assessment of large and small nerve fibre function, CCM, neuropathic symptoms (small fibre neuropathy symptom inventory questionnaire, neuropathic pain scale) and QoL (SF-36, pre-R-ODS and hospital anxiety and depression scale). Patients with painful compared to painless DN, had comparable neurophysiology and vibration perception, but lower corneal nerve fibre density (20.1 ± 0.87 vs. 24.13 ± 0.91, P = 0.005), branch density (44.4 ± 3.31 vs. 57.74 ± 3.98, P = 0.03), length (19.61 ± 0.81 vs. 22.77 ± 0.83, P = 0.01), inferior whorl length (18.03 ± 1.46 vs. 25.1 ± 1.95, P = 0.005) and cold sensation threshold (21.35 ± 0.99 vs. 26.08 ± 0.5, P < 0.0001) and higher warm sensation threshold (43.7 ± 0.49 vs. 41.37 ± 0.51, P = 0.004) indicative of small fibre damage. There was a significant association between all CCM parameters and the severity of painful neuropathic symptoms, depression score and QoL. CCM identifies small nerve fibre loss, which correlates with the severity of neuropathic symptoms and reduced QoL in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures