Does the Interplay of Callous-Unemotional Traits and Moral Disengagement Underpin Disruptive Behavior? A Systematic Review
- PMID: 32099503
- PMCID: PMC7006850
- DOI: 10.2147/AHMT.S151699
Does the Interplay of Callous-Unemotional Traits and Moral Disengagement Underpin Disruptive Behavior? A Systematic Review
Abstract
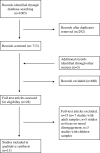
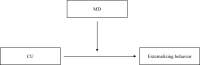
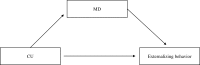
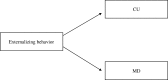
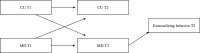
Disruptive behavior could represent an (un)moral behavioral component of multi-dimensional construct of morality that includes affective and cognitive aspects. Thus, it is pivotal to investigate their interplay between affective and cognitive processes the better to understand how to intervene to contrast disruptive behavior and its antisocial outcomes. The present review has examined the relationship between affective and cognitive processes implied in moral functioning by focusing on callous-unemotional traits (CU) and moral disengagement. Starting from 1005 records identified by PsycINFO, Pubmed, and Pubpsych, only 13 studies have been selected. These studies show different theoretical approaches and methodologies and put in evidence the nuances of possible interactions of CU and moral disengagement during adolescence based on different research field. Overall, most of the scholars seem to conclude that different interplay can be plausible, suggesting that it is likely that during the adolescence the influence of moral disengagement and CU is reciprocal and longitudinal. Specifically, in adolescents with Disruptive Behavior Disorders CU and moral disengagement can move together in organizing and becoming chronic of antisocial affective-cognitive system, and in particular moral disengagement may give a free way to engage in disruptive behavior.
Keywords: adolescence; callous-unemotional traits; disruptive behavior; moral disengagement; morality.
© 2020 Paciello et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Moral disengagement and callous-unemotional traits: A longitudinal study of Italian adolescents with a disruptive behaviour disorder.Crim Behav Ment Health. 2017 Dec;27(5):514-524. doi: 10.1002/cbm.2019. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Crim Behav Ment Health. 2017. PMID: 27624802
-
Moral disengagement and callous unemotional traits configurations in adolescents with disruptive behavior disorder: A person-oriented approach.Psychiatry Res. 2017 Dec;258:591-593. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2017.08.043. Epub 2017 Aug 19. Psychiatry Res. 2017. PMID: 28843630
-
Adolescents High in Callous-Unemotional Traits are Prone to be Bystanders: The Roles of Moral Disengagement, Moral Identity, and Perceived Social Support.Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2024 May 13. doi: 10.1007/s10578-024-01709-y. Online ahead of print. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2024. PMID: 38739301
-
Research review: the importance of callous-unemotional traits for developmental models of aggressive and antisocial behavior.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2008 Apr;49(4):359-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2007.01862.x. Epub 2008 Jan 21. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18221345 Review.
-
Neuroimaging findings in disruptive behavior disorders.CNS Spectr. 2015 Aug;20(4):369-81. doi: 10.1017/S1092852914000789. Epub 2015 Apr 10. CNS Spectr. 2015. PMID: 25860779 Review.
Cited by
-
Psychopathic Traits, Externalizing Problems, and Prosocial Behavior: The Role of Social Dominance Orientation.J Clin Med. 2023 May 17;12(10):3521. doi: 10.3390/jcm12103521. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37240627 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent Associations Between Callous-Unemotional Traits, Moral Disengagement, and Bullying Perpetration in Adolescence.J Interpers Violence. 2025 Mar;40(5-6):1459-1483. doi: 10.1177/08862605241260007. Epub 2024 Jun 19. J Interpers Violence. 2025. PMID: 39912440 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of empathy and callous-unemotional traits on externalizing behavior in juvenile offenders: The mediating role of moral disengagement.Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2025 Sep;71(6):1141-1154. doi: 10.1177/00207640251328818. Epub 2025 Mar 31. Int J Soc Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40163024 Free PMC article.
-
Psychopathic Traits in Childhood: Insights from Parental Warmth and Fearless Temperament via Conscience Development.Brain Sci. 2021 Jul 13;11(7):923. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11070923. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 34356157 Free PMC article.
-
The role of anger rumination as a mediator in the relationship between driver moral disengagement and driving angry.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 5;10(8):e29112. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29112. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38644810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steiner H, Remsing L. Practice parameter for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with oppositional defiant disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2007;46(1):126–141. doi:10.1097/01.chi.0000246060.62706.af - DOI - PubMed
-
- Murrihy RC, Kidman AD, Ollendick TH, eds. Clinical Handbook of Assessing and Treating Conduct Problems in Youth. New York: Springer Science & Business Media; 2010.
-
- American Psychiatric Association, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th ed. Text rev Washington, DC: Author; 2000: 223–234.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

