Blood glucose and insulin concentrations after alpha-2-agonists administration in horses with and without insulin dysregulation
- PMID: 32100334
- PMCID: PMC7096659
- DOI: 10.1111/jvim.15747
Blood glucose and insulin concentrations after alpha-2-agonists administration in horses with and without insulin dysregulation
Abstract
Background: In metabolically stable horses, alpha-2-agonists suppress insulin secretion with transient hyperglycemia and rebound hyperinsulinemia. In horses with insulin dysregulation (ID), the effect of alpha-2-agonists has not been investigated; however, both the alpha-2-agonist-induced suppression of insulin secretion and rebound hyperinsulinemia could have clinical relevance.
Hypothesis/objectives: In horses with ID, alpha-2-agonists will alter insulin and glucose dynamics.
Animals: Seven horses with ID and 7 control horses.
Methods: In this randomized crossover study, xylazine hydrochloride (1.1 mg/kg) or detomidine hydrochloride (30 μg/kg) were administered IV, and blood was collected for glucose and insulin concentrations at 0, 15, 30, 45, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, and 300 minutes after administration. Horses received each drug in a random order with a 24-hour washout period between drugs. Percent change in glucose and insulin concentrations was compared between groups, drugs, and over time with P < .05 considered significant.
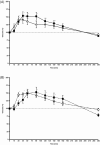
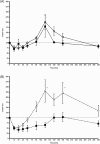
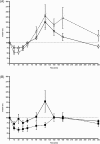
Results: A significant time-dependent effect of both alpha-2-agonists on glucose and insulin concentrations in control and ID horses was identified (P = .01 for all comparisons). There was no significant effect of sedative selection and endocrine status on blood glucose concentration in either group; however, in ID horses, xylazine administration resulted in severe rebound hyperinsulinemia whereas detomidine administration did not (P = .02).
Conclusions and clinical importance: Alpha-2-agonists have a significant effect on glucose and insulin concentrations in horses. In ID horses, detomidine could minimize hyperinsulinemia when compared to xylazine.
Keywords: detomidine; endocrinology; equine; metabolism; pancreas; xylazine.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rohrbach H, Korpivaara T, Schatzmann U, Spadavecchia C. Comparison of the effects of the alpha‐2 agonists detomidine, romifidine and xylazine on nociceptive withdrawal reflex and temporal summation in horses. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2009;36:384‐395. - PubMed
-
- England GC, Clarke KW, Goossens L. A comparison of the sedative effects of three alpha 2‐adrenoceptor agonists (romifidine, detomidine and xylazine) in the horse. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 1992;15:194‐201. - PubMed
-
- Ringer SK, Schwarzwald CC, Portier K, Mauch J, Ritter A, Bettschart‐Wolfensberger R. Blood glucose, acid‐base and electrolyte changes during loading doses of alpha(2)‐adrenergic agonists followed by constant rate infusions in horses. Vet J. 2013;198:684‐689. - PubMed
-
- Hirose H, Maruyama H, Ito K, Kido K, Koyama K, Saruta T. Effects of alpha 2‐ and beta‐adrenergic agonism on glucagon secretion from perfused pancreata of normal and streptozocin‐induced diabetic rats. Metabolism. 1993;42:1072‐1076. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

