Chest Radiographic and CT Findings of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Analysis of Nine Patients Treated in Korea
- PMID: 32100485
- PMCID: PMC7082662
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0132
Chest Radiographic and CT Findings of the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Analysis of Nine Patients Treated in Korea
Abstract
Objective: This study presents a preliminary report on the chest radiographic and computed tomography (CT) findings of the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pneumonia in Korea.
Materials and methods: As part of a multi-institutional collaboration coordinated by the Korean Society of Thoracic Radiology, we collected nine patients with COVID-19 infections who had undergone chest radiography and CT scans. We analyzed the radiographic and CT findings of COVID-19 pneumonia at baseline. Fisher's exact test was used to compare CT findings depending on the shape of pulmonary lesions.
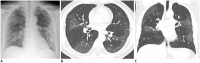
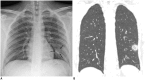
Results: Three of the nine patients (33.3%) had parenchymal abnormalities detected by chest radiography, and most of the abnormalities were peripheral consolidations. Chest CT images showed bilateral involvement in eight of the nine patients, and a unilobar reversed halo sign in the other patient. In total, 77 pulmonary lesions were found, including patchy lesions (39%), large confluent lesions (13%), and small nodular lesions (48%). The peripheral and posterior lung fields were involved in 78% and 67% of the lesions, respectively. The lesions were typically ill-defined and were composed of mixed ground-glass opacities and consolidation or pure ground-glass opacities. Patchy to confluent lesions were primarily distributed in the lower lobes (p = 0.040) and along the pleura (p < 0.001), whereas nodular lesions were primarily distributed along the bronchovascular bundles (p = 0.006).
Conclusion: COVID-19 pneumonia in Korea primarily manifested as pure to mixed ground-glass opacities with a patchy to confluent or nodular shape in the bilateral peripheral posterior lungs. A considerable proportion of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia had normal chest radiographs.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chest X-ray; Computed tomography; Coronavirus; Pneumonia.
Copyright © 2020 The Korean Society of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Comment in
-
Key Considerations for Radiologists When Diagnosing the Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19).Korean J Radiol. 2020 May;21(5):625-626. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0190. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Korean J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32207256 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report-27. World Health Organization Web site; 2020. Feb 17, [Accessed February 17, 2020]. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2....
-
- Song F, Shi N, Shan F, Zhang Z, Shen J, Lu H, et al. Emerging coronavirus 2019-nCoV pneumonia. Radiology. 2020 Feb 06; doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020200274. [Epub] - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

