Epigallocatechin-3-gallate Inhibits Cu(II)-Induced β-2-Microglobulin Amyloid Formation by Binding to the Edge of Its β-Sheets
- PMID: 32100530
- PMCID: PMC7080597
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00043
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate Inhibits Cu(II)-Induced β-2-Microglobulin Amyloid Formation by Binding to the Edge of Its β-Sheets
Abstract
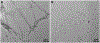
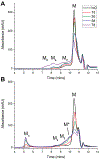
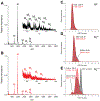
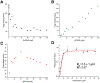
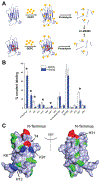
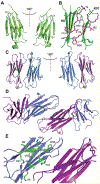
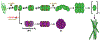
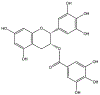
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) is a catechin found in green tea that can inhibit the amyloid formation of a wide variety of proteins. EGCG's ability to prevent or redirect the amyloid formation of so many proteins may reflect a common mechanism of action, and thus, greater molecular-level insight into how it exerts its effect could have broad implications. Here, we investigate the molecular details of EGCG's inhibition of the protein β-2-microglobulin (β2m), which forms amyloids in patients undergoing long-term dialysis treatment. Using size-exclusion chromatography and a collection of mass spectrometry-based techniques, we find that EGCG prevents Cu(II)-induced β2m amyloid formation by diverting the normal progression of preamyloid oligomers toward the formation of spherical, redissolvable aggregates. EGCG exerts its effect by binding with a micromolar affinity (Kd ≈ 5 μM) to the β2m monomer on the edge of two β-sheets near the N-terminus. This interaction destabilizes the preamyloid dimer and prevents the formation of a tetramer species previously shown to be essential for Cu(II)-induced β2m amyloid formation. EGCG's binding at the edge of the β-sheets in β2m is consistent with a previous hypothesis that EGCG generally prevents amyloid formation by binding cross-β-sheet aggregation intermediates.
Figures
References
-
- Ozdal T, Capanoglu E, and Altay F (2013) A review on protein–phenolic interactions and associated changes. Food Res. Int 51, 954–970.
-
- Tanaka T, Ishii T, Mizuno D, Mori T, Yamaji R, Nakamura Y, Kumazawa S, Nakayama T, and Akagawa M (2011) (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses growth of AZ521 human gastric cancer cells by targeting the DEAD-box RNA helicase p68. Free Radic. Biol. Med 50, 1324–1335. - PubMed
-
- Tachibana H, Koga K, Fujimura Y, and Yamada K (2004) A receptor for green tea polyphenol EGCG. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 11, 380–381. - PubMed
-
- Cheng B, Gong H, Xiao H, Petersen RB, Zheng L, and Huang K (2013) Inhibiting toxic aggregation of amyloidogenic proteins: A therapeutic strategy for protein misfolding diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Gen. Subj 1830, 4860–4871. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

