Structural Effect on Adjuvanticity of Saponins
- PMID: 32101001
- PMCID: PMC8832471
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b02063
Structural Effect on Adjuvanticity of Saponins
Abstract
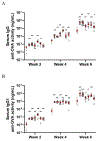
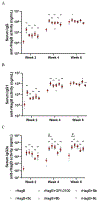
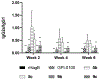
We have prepared a number of saponin-based vaccine adjuvant candidates. These unnatural saponins have a different terminal-functionalized side chain incorporated into the glucuronic acid unit that is attached to a triterpenoid core at its C3 position. The semisynthetic saponin adjuvants have shown significantly different immunostimulatory activities, suggesting that the structure of the side chain, triterpenoid core, and oligosaccharide domain together orchestrate saponin adjuvant's potentiation of immune responses. Among these new adjuvant candidates, VSA-2 (5b), a derivative of Momordica saponin (MS) II, showed consistent enhancement of immunoglobulin G2a (IgG2a) production when it was in formulation with either ovalbumin or recombinant hemagglutinin B (rHagB) antigen. With rHagB antigen, it induced a significantly higher IgG2a response than the positive control GPI-0100, a well-studied semisynthetic saponin adjuvant mixture derived from Quillaja saponaria Molina saponins, known for its ability to induce a balanced Th1/Th2 immunity. These results confirm that Momordica saponins are a viable natural source to provide potent saponin adjuvants after simple chemical derivatization and identify VSA-2 (5b) as another MS-based promising immunostimulant lead owing to its distinctive ability in potentiating the IgG2a response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): P.W. is inventor on patent applications based on this work.
Figures
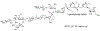

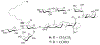


Similar articles
-
Development of semisynthetic saponin immunostimulants.Med Chem Res. 2024;33(8):1292-1306. doi: 10.1007/s00044-024-03227-x. Epub 2024 May 18. Med Chem Res. 2024. PMID: 39132259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of a QS-17/18-Based Vaccine Adjuvant.J Med Chem. 2019 Feb 14;62(3):1669-1676. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01997. Epub 2019 Jan 18. J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30656932 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine Adjuvants Derivatized from Momordica Saponins I and II.J Med Chem. 2019 Nov 14;62(21):9976-9982. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01511. Epub 2019 Oct 28. J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31657920 Free PMC article.
-
Development of semisynthetic triterpenoid saponin derivatives with immune stimulating activity.Vaccine. 2000 Jul 15;18(27):3141-51. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(00)00118-3. Vaccine. 2000. PMID: 10856794
-
Elucidating the Mechanisms of Action of Saponin-Derived Adjuvants.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Jun;39(6):573-585. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.03.005. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29655658 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing Protective Antibodies against Opioids through Antigen Display on Virus-like Particles.Bioconjug Chem. 2024 Feb 21;35(2):164-173. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.3c00415. Epub 2023 Dec 19. Bioconjug Chem. 2024. PMID: 38113481 Free PMC article.
-
Development of semisynthetic saponin immunostimulants.Med Chem Res. 2024;33(8):1292-1306. doi: 10.1007/s00044-024-03227-x. Epub 2024 May 18. Med Chem Res. 2024. PMID: 39132259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunological and Toxicological Assessment of Triterpenoid Saponins Bearing Lewis-X- and QS-21-Based Trisaccharides.Chemistry. 2025 May 19;31(28):e202500994. doi: 10.1002/chem.202500994. Epub 2025 Apr 21. Chemistry. 2025. PMID: 40192644 Free PMC article.
-
Natural and Synthetic Saponins as Vaccine Adjuvants.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Mar 5;9(3):222. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9030222. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33807582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Wild Yam Root (Dioscorea villosa) Extract on the Gene Expression Profile of Triple-negative Breast Cancer Cells.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2021 Nov-Dec;18(6):735-755. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20294. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 34697066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kensil CR; Mo AX; Truneh A Current vaccine adjuvants: An overview of a diverse class. Frontiers in Bioscience 2004, 9, 2972–2988. - PubMed
-
- Leroux-Roels G Unmet needs in modern vaccinology: adjuvants to improve the immune response. Vaccine 2010, 28 Suppl 3, C25–36. - PubMed
-
- Sharp FA; Lavelle EC: Discovery of Vaccine Adjuvants. In Development of Therapeutic Agents Handbook; 1st ed.; Gad SC, Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc: Hoboken, NJ, 2012; pp 533–546.
-
- Wang W Selection of adjuvants for enhanced vaccine potency. World J. Vaccines 2011, 01, 33–78.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

