A New Equation for Calculation of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Patients With Normolipidemia and/or Hypertriglyceridemia
- PMID: 32101259
- PMCID: PMC7240357
- DOI: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.0013
A New Equation for Calculation of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Patients With Normolipidemia and/or Hypertriglyceridemia
Erratum in
-
Errors in Figures.JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May 1;5(5):613. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.0526. JAMA Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32211817 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), a key cardiovascular disease marker, is often estimated by the Friedewald or Martin equation, but calculating LDL-C is less accurate in patients with a low LDL-C level or hypertriglyceridemia (triglyceride [TG] levels ≥400 mg/dL).
Objective: To design a more accurate LDL-C equation for patients with a low LDL-C level and/or hypertriglyceridemia.
Design, setting, and participants: Data on LDL-C levels and other lipid measures from 8656 patients seen at the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center between January 1, 1976, and June 2, 1999, were analyzed by the β-quantification reference method (18 715 LDL-C test results) and were randomly divided into equally sized training and validation data sets. Using TG and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol as independent variables, multiple least squares regression was used to develop an equation for very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, which was then used in a second equation for LDL-C. Equations were tested against the internal validation data set and multiple external data sets of either β-quantification LDL-C results (n = 28 891) or direct LDL-C test results (n = 252 888). Statistical analysis was performed from August 7, 2018, to July 18, 2019.
Main outcomes and measures: Concordance between calculated and measured LDL-C levels by β-quantification, as assessed by various measures of test accuracy (correlation coefficient [R2], root mean square error [RMSE], mean absolute difference [MAD]), and percentage of patients misclassified at LDL-C treatment thresholds of 70, 100, and 190 mg/dL.
Results: Compared with β-quantification, the new equation was more accurate than other LDL-C equations (slope, 0.964; RMSE = 15.2 mg/dL; R2 = 0.9648; vs Friedewald equation: slope, 1.056; RMSE = 32 mg/dL; R2 = 0.8808; vs Martin equation: slope, 0.945; RMSE = 25.7 mg/dL; R2 = 0.9022), particularly for patients with hypertriglyceridemia (MAD = 24.9 mg/dL; vs Friedewald equation: MAD = 56.4 mg/dL; vs Martin equation: MAD = 44.8 mg/dL). The new equation calculates the LDL-C level in patients with TG levels up to 800 mg/dL as accurately as the Friedewald equation does for TG levels less than 400 mg/dL and was associated with 35% fewer misclassifications when patients with hypertriglyceridemia (TG levels, 400-800 mg/dL) were categorized into different LDL-C treatment groups.
Conclusions and relevance: The new equation can be readily implemented by clinical laboratories with no additional costs compared with the standard lipid panel. It will allow for more accurate calculation of LDL-C level in patients with low LDL-C levels and/or hypertriglyceridemia (TG levels, ≤800 mg/dL) and thus should improve the use of LDL-C level in cardiovascular disease risk management.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
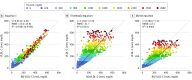
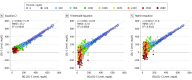
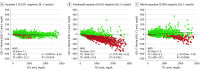
Comment in
-
Methods of Calculating Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level.JAMA Cardiol. 2020 May 1;5(5):502-503. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.0042. JAMA Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32101263 No abstract available.
-
Accuracy of New Equation to Calculate Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol-Reply.JAMA Cardiol. 2021 Jan 1;6(1):122-123. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.4445. JAMA Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 32997101 No abstract available.
-
Accuracy of New Equation to Calculate Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol.JAMA Cardiol. 2021 Jan 1;6(1):121-122. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.4411. JAMA Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 32997104 No abstract available.
-
Accuracy of New Equation to Calculate Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol.JAMA Cardiol. 2021 Jan 1;6(1):121. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.4408. JAMA Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 32997117 No abstract available.
References
-
- Langlois MR, Chapman MJ, Cobbaert C, et al. ; European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) and the European Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (EFLM) Joint Consensus Initiative . Quantifying atherogenic lipoproteins: current and future challenges in the era of personalized medicine and very low concentrations of LDL cholesterol: a consensus statement from EAS and EFLM. Clin Chem. 2018;64(7):1006-1033. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2018.287037 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

