Enhancement by TNF-α of TTX-resistant NaV current in muscle sensory neurons after femoral artery occlusion
- PMID: 32101460
- PMCID: PMC7191414
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00338.2019
Enhancement by TNF-α of TTX-resistant NaV current in muscle sensory neurons after femoral artery occlusion
Abstract
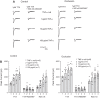
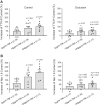
Femoral artery occlusion in rats has been used to study human peripheral artery disease (PAD). Using this animal model, a recent study suggests that increases in levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and its receptor lead to exaggerated responses of sympathetic nervous activity and arterial blood pressure as metabolically sensitive muscle afferents are activated. Note that voltage-dependent Na+ subtype NaV1.8 channels (NaV1.8) are predominately present in chemically sensitive thin fiber sensory nerves. The purpose of this study was to examine the role played by TNF-α in regulating activity of NaV1.8 currents in muscle dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons of rats with PAD induced by femoral artery occlusion. DRG neurons from control and occluded limbs of rats were labeled by injecting the fluorescent tracer DiI into the hindlimb muscles 5 days before the experiments. A voltage patch-clamp mode was used to examine TTX-resistant (TTX-R) NaV currents. Results were as follows: 72 h of femoral artery occlusion increased peak amplitude of TTX-R [1,922 ± 139 pA in occlusion (n = 11 DRG neurons) vs. 1,178 ± 39 pA in control (n = 10), means ± SE; P < 0.001 between the 2 groups] and NaV1.8 currents [1,461 ± 116 pA in occlusion (n = 11) and 766 ± 48 pA in control (n = 10); P < 0.001 between groups] in muscle DRG neurons. TNF-α exposure amplified TTX-R and NaV1.8 currents in DRG neurons of occluded muscles in a dose-dependent manner. Notably, the amplification of TTX-R and NaV1.8 currents induced by TNF-α was attenuated in DRG neurons with preincubation with respective inhibitors of the intracellular signaling pathways p38-MAPK, JNK, and ERK. In conclusion, our data suggest that NaV1.8 is engaged in the role of TNF-α in amplifying muscle afferent inputs as the hindlimb muscles are ischemic; p38-MAPK, JNK, and ERK pathways are likely necessary to mediate the effects of TNF-α.
Keywords: NaV1.8 channels; TNF-α; dorsal root ganglion neuron; muscle afferent; peripheral artery disease.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

