Personality types in individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 32101526
- PMCID: PMC7077523
- DOI: 10.1530/EC-19-0499
Personality types in individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Objective: The Type A personality, characterized by impatience, strong career ambition and competitiveness, is associated with greater sensitivity to external stress. Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an auto-immune disease, which is potentially influenced by stress, unlike type 2 diabetes (T2D). The aim of this study was to assess whether individuals with T1D and T2D exhibited significant differences on the Type A personality scale. We also assessed personality in patients with thyroid auto-immune diseases to validate potential links between auto-immune disease and Type A personality.
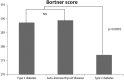
Design and methods: The Bortner questionnaire was used to assess Type A personality in 188 patients with T1D, 430 patients with T2D and 85 patients with auto-immune thyroid disease (Graves' disease or Hashimoto's thyroiditis).
Results: Type A Bortner scores were significantly higher in T1D patients than in T2D patients (188 ± 34 vs 177 ± 36, P < 0.0001). Patients with auto-immune thyroid diseases and T1D patients had similar Type A Bortner scores (189 ± 33 vs 188 ± 34, P = 0.860).
Conclusion: Patients with auto-immune T1D have higher Type A scores than T2D patients. Furthermore, patients with auto-immune thyroid disease also have elevated Type A scores similar to those observed in type 1 diabetes, suggesting that an elevated Type A score in T1D is potentially related to its auto-immune origin. This suggests a possible link between Type A personality and auto-immune diseases via stress-triggering psychobiological pathways. The different personality score between T1D and T2D is an important factor, which could influence self-care coping strategies in diabetes and long-term prognosis.
Keywords: auto-immunity; diabetes mellitus; thyroid disease; type A personality.
Figures
References
-
- Chauvet-Gélinier JC, Trojak B, Lemogne C, Aho-Glélé LS, Brindisi MC, Bouillet B, Ponavoy E, Meille V, Simoneau I, Chahraoui K, et al Potential influence of Type A personality on plasma C-reactive protein levels in people with diabetes. Diabetes and Metabolism 2016. 42 88–95. ( 10.1016/j.diabet.2015.08.001) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Franco-Belge GC. Facteurs psychologiques et cardiopathies ischémiques. Annales de Cardiologie and d’Angeiologie 1983. 32 295–302. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources