Identification and quantification of cassava starch adulteration in different food starches by droplet digital PCR
- PMID: 32101546
- PMCID: PMC7043801
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228624
Identification and quantification of cassava starch adulteration in different food starches by droplet digital PCR
Abstract
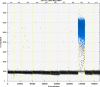
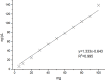
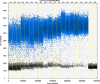
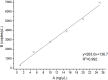
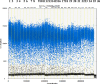
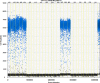
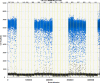
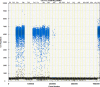
We report a rapid and accurate quantitative detection method using droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) technology to identify cassava adulteration in starch products. The ddPCR analysis showed that the weight of cassava (M) and cassava-extracted DNA content had a significant linear relationship-the correlation coefficient was R2 = 0.995, and the maximum coefficient of variation of replicates was 7.48%. The DNA content and DNA copy number (C) measured by ddPCR also had a linear relationship with R2 = 0.992; the maximum coefficient of variation of replicates was 8.85%. The range of cassava ddPCR DNA content was 25 ng/μL, and the formula M = (C + 32.409)/350.579 was obtained by converting DNA content into the median signal. The accuracy and application potential of the method were verified using the constructed adulteration model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
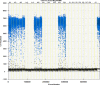
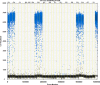
References
-
- Xu ZQ. Quick identification of starch adulteration. China Quality Supervision, 2005, 8: 45 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1607.2005.08.025 - DOI
-
- Wang SQ, Gao X, Lan QF, Lin Li, Wang LL, Yang YL, et al. Identification of tapioca starch and sweet potato starch in adulterated glutinous rice powder-differential scanning calorimetry[J]. Food Industry Technology, 2015, 36 (13): 325–328+333.
-
- Ali ME, Hashim U, Mustafa S, Man YBC, Dhahi TS, Kashif M, et al. Analysis of pork adulteration in commercial meatballs targeting porcine-specific mitochondrial cytochrome b gene by TaqMan probe real-time polymerase chain reaction. Meat Scie 2012;91:454–459. 10.1016/j.meatsci.2012.02.031. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

