Dop1R1, a type 1 dopaminergic receptor expressed in Mushroom Bodies, modulates Drosophila larval locomotion
- PMID: 32101569
- PMCID: PMC7043742
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229671
Dop1R1, a type 1 dopaminergic receptor expressed in Mushroom Bodies, modulates Drosophila larval locomotion
Abstract
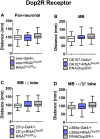
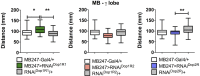
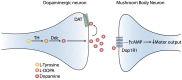
As in vertebrates, dopaminergic neural systems are key regulators of motor programs in insects, including the fly Drosophila melanogaster. Dopaminergic systems innervate the Mushroom Bodies (MB), an important association area in the insect brain primarily associated to olfactory learning and memory, but that has been also implicated with the execution of motor programs. The main objectives of this work is to assess the idea that dopaminergic systems contribute to the execution of motor programs in Drosophila larvae, and then, to evaluate the contribution of specific dopaminergic receptors expressed in MB to these programs. Our results show that animals bearing a mutation in the dopamine transporter show reduced locomotion, while mutants for the dopaminergic biosynthetic enzymes or the dopamine receptor Dop1R1 exhibit increased locomotion. Pan-neuronal expression of an RNAi for the Dop1R1 confirmed these results. Further studies show that animals expressing the RNAi for Dop1R1 in the entire MB neuronal population or only in the MB γ-lobe forming neurons, exhibit an increased motor output, as well. Interestingly, our results also suggest that other dopaminergic receptors do not contribute to larval motor behavior. Thus, our data support the proposition that CNS dopamine systems innervating MB neurons modulate larval locomotion and that Dop1R1 mediates this effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Meder D, Herz DM, Rowe JB, Lehericy S, Siebner HR. The role of dopamine in the brain—lessons learned from Parkinson's disease. Neuroimage. 2018. - PubMed
-
- Chang HY, Grygoruk A, Brooks ES, Ackerson LC, Maidment NT, Bainton RJ, et al. Overexpression of the Drosophila vesicular monoamine transporter increases motor activity and courtship but decreases the behavioral response to cocaine. Mol Psychiatry. 2006;11(1):99–113. 10.1038/sj.mp.4001742 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

