Predicting Successful Generation and Inhibition of Seizure-like Afterdischarges and Mapping Their Seizure Networks Using fMRI
- PMID: 32101734
- PMCID: PMC8720841
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.01.095
Predicting Successful Generation and Inhibition of Seizure-like Afterdischarges and Mapping Their Seizure Networks Using fMRI
Abstract
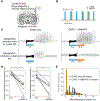
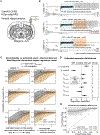
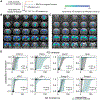
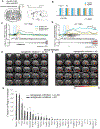
To understand the conditions necessary to initiate and terminate seizures, we investigate optogenetically induced hippocampal seizures with LFP, fMRI, and optogenetic inhibition. During afterdischarge induction using optogenetics, LFP recordings show that stimulations with earlier ictal onset times are more likely to result in afterdischarges and are more difficult to curtail with optogenetic inhibition. These results are generalizable across two initiation sites, the dorsal and ventral hippocampus. fMRI shows that afterdischarges initiated from the dorsal or ventral hippocampus exhibit distinct networks. Short-duration seizures initiated in the dorsal and ventral hippocampus are unilateral and bilateral, respectively, while longer-duration afterdischarges recruit broader, bilateral networks. When optogenetic inhibition is ineffective at stopping seizures, the network activity spreads more extensively but largely overlaps with the network activity associated with seizures that could be curtailed. These results provide insights into how seizures can be inhibited, which has implications for targeted seizure interventions.
Keywords: afterdischarge; epilepsy; fMRI; generation; hippocampus; inhibition; network; optogenetrics; seizure; stopping.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests J.H.L. is a founder of LVIS.
Figures



References
-
- Allen PJ, Josephs O, and Turner R (2000). A method for removing imaging artifact from continuous EEG recorded during functional MRI. NeuroImage 12, 230–239. - PubMed
-
- Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, and Walker S (2014). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. arXiv preprint arXiv:14065823.
-
- Christie IN, Wells JA, Southern P, Marina N, Kasparov S, Gourine AV, and Lythgoe MF (2013). fMRI response to blue light delivery in the naive brain: implications for combined optogenetic fMRI studies. Neuroimage 66, 634–641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

