Adaptive Evolution Targets a piRNA Precursor Transcription Network
- PMID: 32101744
- PMCID: PMC7061269
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.01.109
Adaptive Evolution Targets a piRNA Precursor Transcription Network
Abstract
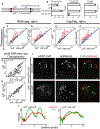
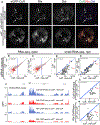
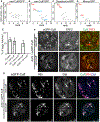
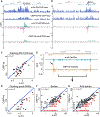
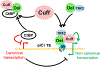
In Drosophila, transposon-silencing piRNAs are derived from heterochromatic clusters and a subset of euchromatic transposon insertions, which are bound by the Rhino-Deadlock-Cutoff complex. The HP1 homolog Rhino binds to Deadlock, which recruits TRF2 to promote non-canonical transcription from both genomic strands. Cuff function is less well understood, but this Rai1 homolog shows hallmarks of adaptive evolution, which can remodel functional interactions within host defense systems. Supporting this hypothesis, Drosophila simulans Cutoff is a dominant-negative allele when expressed in Drosophila melanogaster, in which it traps Deadlock, TRF2, and the conserved transcriptional co-repressor CtBP in stable complexes. Cutoff functions with Rhino and Deadlock to drive non-canonical transcription. In contrast, CtBP suppresses canonical transcription of transposons and promoters flanking the major germline clusters, and canonical transcription interferes with downstream non-canonical transcription and piRNA production. Adaptive evolution thus targets interactions among Cutoff, TRF2, and CtBP that balance canonical and non-canonical piRNA precursor transcription.
Keywords: CtBP; Cutoff; TRF2; adaptive evolution; cross-species complementation; piRNA cluster transcriptional regulation; piRNA pathway; transposon silencing.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

