Combined Small and Squamous Transformation in EGFR-mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 32101830
- PMCID: PMC7303443
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.3542-19
Combined Small and Squamous Transformation in EGFR-mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
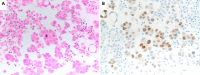
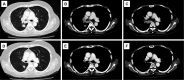
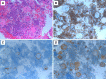
Histologic transformation has been described as an acquired mechanism of resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). We herein report the case of a woman with stage IV lung adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR exon 19 deletions who was initially treated with EGFR-TKIs; several cytotoxic chemotherapeutic regimens were used when resistance developed. A lymph node re-biopsy revealed histologic transformation of the tumor to combined small-cell lung cancer and squamous cell carcinoma with retained EGFR exon 19 deletions. Following sequential chemotherapy appropriate for transformed histology, a clinical response was achieved.
Keywords: EGFR mutation; acquired resistance; histologic transformation; non-small-cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Mikio Takamori: Honoraria, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly Japan, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Ono Pharmaceutical, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim Japan, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Kyorin Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Novartis, Astellas and Qiagen.
Figures
References
-
- Li W, Ren S, Li J, et al. T790M mutation is associated with better efficacy of treatment beyond progression with EGFR-TKI in advanced NSCLC patients. Lung Cancer 84: 295-300, 2014. - PubMed
-
- Brugger W, Thomas M. EGFR-TKI resistant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): new developments and implications for future treatment. Lung Cancer 77: 2-8, 2012. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

