Enzymatic Degradation of p-Nitrophenyl Esters, Polyethylene Terephthalate, Cutin, and Suberin by Sub1, a Suberinase Encoded by the Plant Pathogen Streptomyces scabies
- PMID: 32101840
- PMCID: PMC7104285
- DOI: 10.1264/jsme2.ME19086
Enzymatic Degradation of p-Nitrophenyl Esters, Polyethylene Terephthalate, Cutin, and Suberin by Sub1, a Suberinase Encoded by the Plant Pathogen Streptomyces scabies
Abstract
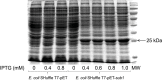
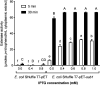
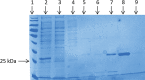
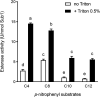
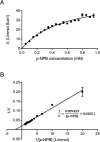
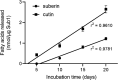
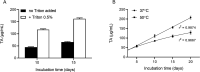
The genome of Streptomyces scabies, the predominant causal agent of potato common scab, encodes a potential cutinase, the protein Sub1, which was previously shown to be specifically induced in the presence of suberin. The sub1 gene was expressed in Escherichia coli and the recombinant protein Sub1 was purified and characterized. The enzyme was shown to be versatile because it hydrolyzes a number of natural and synthetic substrates. Sub1 hydrolyzed p-nitrophenyl esters, with the hydrolysis of those harboring short carbon chains being the most effective. The Vmax and Km values of Sub1 for p-nitrophenyl butyrate were 2.36 mol g-1 min-1 and 5.7 10-4 M, respectively. Sub1 hydrolyzed the recalcitrant polymers cutin and suberin because the release of fatty acids from these substrates was observed following the incubation of the enzyme with these polymers. Furthermore, the hydrolyzing activity of the esterase Sub1 on the synthetic polymer polyethylene terephthalate (PET) was demonstrated by the release of terephthalic acid (TA). Sub1 activity on PET was markedly enhanced by the addition of Triton and was shown to be stable at 37°C for at least 20 d.
Keywords: actinobacteria; common scab; cutinase; esterase; potato.
Figures
References
-
- Beauséjour J., Goyer C., Vachon J., and Beaulieu C. (1999) Production of thaxtomin A by Streptomyces scabies strains in plant extract containing media. Can J Microbiol 45: 764–768.
-
- Beisson F., Li-Beisson Y., and Pollard M. (2012) Solving the puzzles of cutin and suberin polymer biosynthesis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 15: 329–337. - PubMed
-
- Bernards M.A., and Lewis N.G. (1998) The macromolecular aromatic domain in suberized tissue: a changing paradigm. Phytochemistry 47: 915–933. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

