Improvement Effect of Lotus Leaf Flavonoids on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury in Mice
- PMID: 32102401
- PMCID: PMC7169453
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines8020041
Improvement Effect of Lotus Leaf Flavonoids on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury in Mice
Abstract
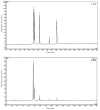
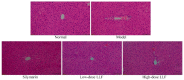
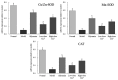
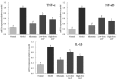
In this study, the effect of lotus leaf flavonoids (LLF) on carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver injury in mice was studied. CCl4 was injected intraperitoneally to induce liver injury in Kunming mice. Mice were treated with LLF by gavage, and the mRNA expression levels in serum and liver were detected. Compared with the model group, LLF significantly reduced the liver index and serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), triglyceride (TG), and total cholesterol (TC) levels in mice with CCl4-induced liver injury. Pathological observation showed that LLF effectively reduced morphological incompleteness and hepatocyte necrosis in CCl4-treated liver tissue. The result of quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) indicated that LLF significantly up-regulated the mRNA expression levels of copper/zinc superoxide dismutase (Cu/Zn-SOD), manganese superoxide dismutase (Mn-SOD), and catalase (CAT) and down- regulated the expression levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) (p < 0.05). Thus, LLF is an active ingredient that ameliorates liver injury, and it has good application prospect.
Keywords: carbon tetrachloride; liver injury; lotus leaf flavonoids; mRNA, mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Yin L.H., Yu H., Peng J.Y. Molecular Mechanism and Intervention of Chinese Medicine of Carbon Tetrachloride Induced Liver Injury. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 2015;32:1147–1155.
-
- Tittarelli R., Pellegrini M., Scarpellini M.G., Marinelli E., Bruti V., di Luca N.M., Busardò F.P., Zaami S. Hepatotoxicity of paracetamol and related fatalities. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017;21:95–101. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

